Background on aelf
The story of aelf began on 10 December 2017, when aelf's vision and plans were introduced to global investors at a Coindesk conference. aelf successfully completed its fund-raising significantly ahead of schedule, having secured investments from notable institutions such as Binance, Arrington Capital, Draper Dragon, Galaxy Digital etc. In the same month, the ELF token was listed on six major exchanges, including Binance and OKEX. aelf Testnet was successfully launched in 2018, followed by another successful launch of the Mainnet in 2020.
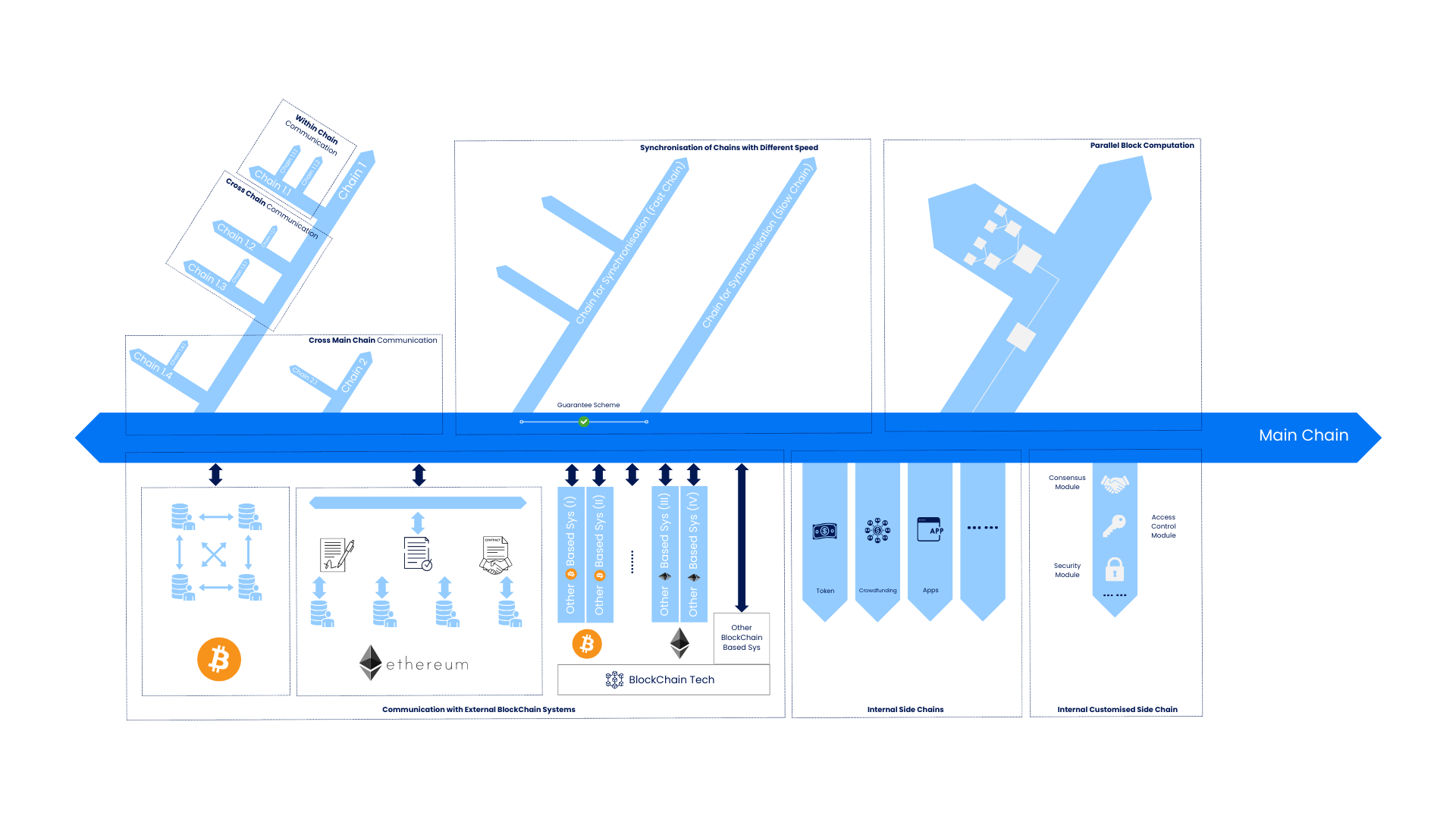
aelf is primarily a multi-chain parallel computing blockchain framework which was created to address several of the limitations of traditional blockchain systems, such as performance bottlenecks and data complexity. aelf's vision is to be a "Linux Ecosystem" equivalent for a blockchain that incorporates state of the art IT design principles, which in particular allows developers to customise Chains to meet their own needs. At its core, aelf contains the following main features:
- MainChain and multi-layer dAppChains to handle various user driven scenarios. One chain is designed for one use case, distributing different tasks on multiple chains, which improves processing efficiency.
- Communication with external blockchain networks, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, via cross chain messaging protocols.
- Parallel processing for non-competing transactions in a cloud-based environment.
- Basic components for a minimum viable Block and Genesis Smart Contract Collection for each Chain, which reduces data complexity and allows for high customisation at the same time.
- Permission for stakeholders to approve amendments to the protocol, including redefining the Consensus Protocol; Permission for dAppChains to join or exit from MainChain dynamically based on the Consensus Protocol.
aelf's primary strength lies in its architecture, which utilises a multi-layered structure comprising a MainChain and multiple dAppChains. This differs from a traditional Single Chain system in that aelf is a "Branched Ecosystem", where the MainChain works as the backbone of the system and connects to multiple dAppChains. Compared with the traditional "one Chain to any type of Contract", aelf's "One Chain to one type of Contract" design allows aelf to distribute tasks efficiently and process transactions in parallel, significantly enhancing scalability and reducing congestion. At the same time, the dAppChains are easier to manage and can be tailored for specific applications, enabling aelf to support a wide range of use cases without compromising performance.
For aelf's consensus mechanism, it utilises the Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) to manage overall network efficiency. DPoS is known for its speed and energy efficiency compared to other consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW). By allowing token holders to vote for delegates who validate transactions and maintain the network, aelf ensures a high level of security and decentralisation while keeping transaction times low. Additionally, aelf's dynamic indexing and comprehensive token system offer robust support for various applications, from digital asset management to DeFi platforms, making it a versatile and powerful blockchain solution for all types of developers.
Last but not least, the C# programming language forms the foundation of the entire aelf blockchain. C# is a robust, object-oriented language with strong type-checking, which enhances code reliability and reduces runtime errors and are crucial for the immutable and secure nature of blockchain applications. Its performance characteristics, including efficient memory management and speed, are beneficial for blockchain's demanding requirements. Further, C#'s support for asynchronous programming and parallel processing helps optimise the performance of blockchain nodes, ensuring they can handle multiple transactions simultaneously without significant latency. This strong technical foundation underpins aelf's ability to handle high transaction volumes and complex operations with ease.
For further details on aelf's original design and architecture, please kindly refer to our original whitepaper.