Operational Excellence
i) Machine Learning Models for Smart Contract Optimisation
Integrating machine learning models into the aelf blockchain can significantly optimise gas usage and execution efficiency. We draw inspiration from existing rollup technologies but enhance them through advanced predictive modelling.
Optimising Gas Usage
Machine learning models can analyee historical data on smart contract executions to identify patterns and predict the optimal gas prices for future transactions. This approach is similar to the predictive models used in financial markets to forecast asset prices and trading volumes, ensuring that transactions on aelf are both cost-effective and timely. Another practical application for machine learning models is the detection and minimisation of gas-expensive patterns in smart contract code. aelf has adapted tools that use machine learning algorithms to analyse and identify inefficient code patterns that consume excessive gas. For example, replacing arrays with mappings where iteration is not required can significantly reduce gas costs, as mappings are generally less expensive in terms of gas usage. By continuously monitoring and optimising these patterns, aelf can ensure that smart contracts are executed with minimal gas expenditure, similar to optimisation techniques employed by developers on the Ethereum network.
Moreover, machine learning can optimise the execution efficiency of smart contracts by dynamically adjusting resource allocation based on the predicted computational requirements. Techniques such as variable packing, which arranges variables to fit into fewer storage slots, can be automatically identified and applied by machine learning algorithms. This reduces the number of storage operations needed, thereby lowering gas consumption. Additionally, employing machine learning on aelf to manage on-chain and off-chain data storage decisions can optimise the use of memory and storage, further enhancing gas efficiency.
Enhancing Execution Efficiency
Beyond gas optimisation, AI can also streamline the execution efficiency of smart contracts on aelf. By employing predictive modelling, AI can anticipate resource requirements and execution paths for complex smart contracts. This foresight allows the system to allocate computational resources more effectively, ensuring that contracts run smoothly without unnecessary delays. This can be seen today in how Google Cloud’s AI optimises resource allocation for its cloud services. By using machine learning models to predict demand, Google Cloud can dynamically adjust resource allocation to meet user needs efficiently. In the case of aelf, this involves using AI to forecast transaction volumes and adjust computational resources in real-time. During a DeFi surge for instance, AI models can predict increased transaction loads and preemptively allocate more computational power to handle the surge without network slowdowns.
Predictive models can evaluate the execution patterns of different smart contracts and suggest optimisations in their code to reduce execution time and resource consumption. This is similar to the optimisation techniques used in compiler design, where code is analysed and restructured to improve performance. Another real-life example of this concept is the work done by the Ethereum Foundation to optimise the EVM. Researchers have used AI to analyse smart contract bytecode, detect inefficient loops or redundant calculations and suggest optimisations that reduce gas usage and execution time. By applying similar techniques, aelf can enhance the efficiency of its smart contracts.
ii) AI Oracle on aelf
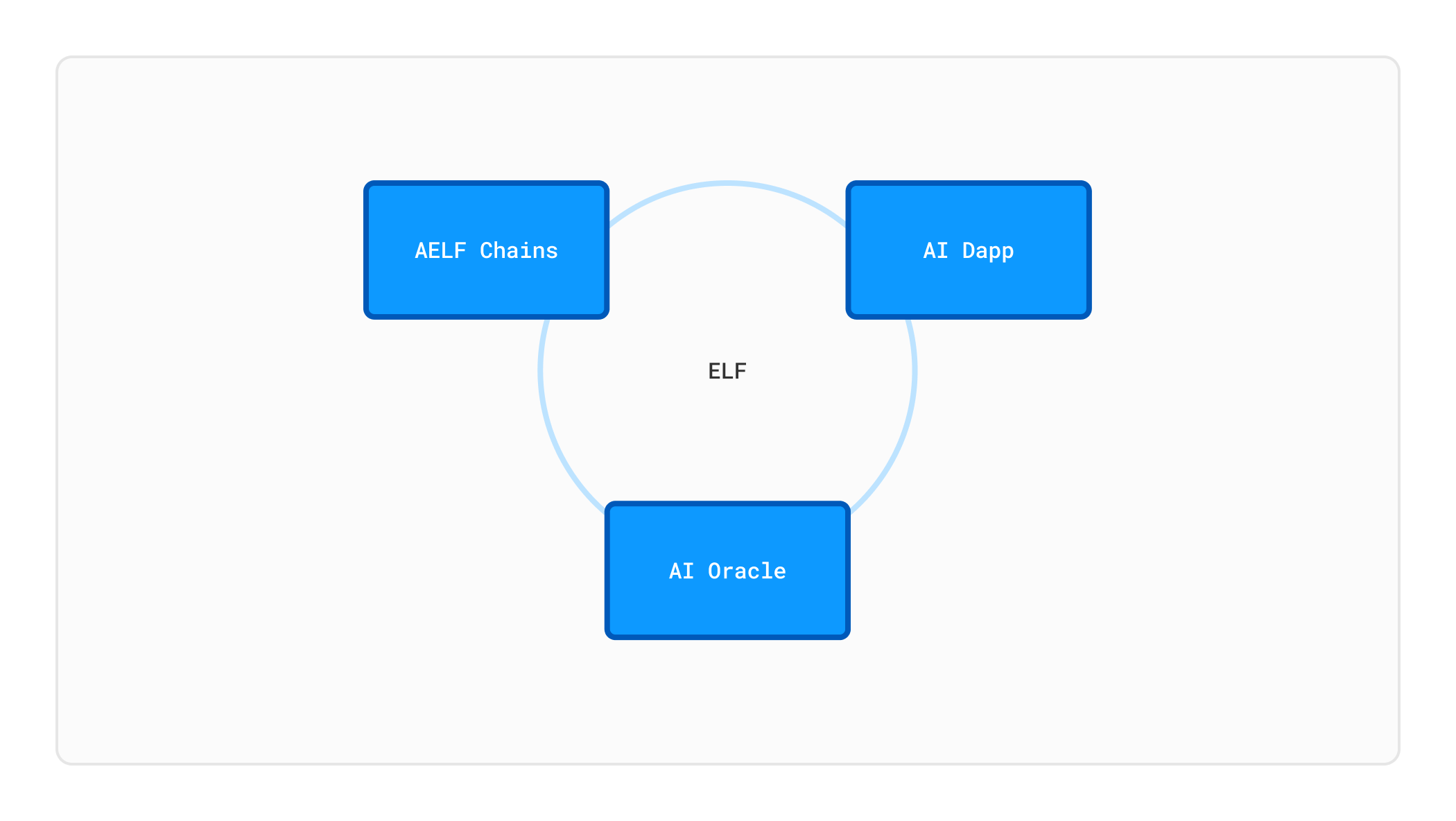
aelf's AI oracle positions itself as the AI layer of Web3, leveraging both oracle and security compute technology to facilitate the development of AI-powered dApps. It plays a crucial role in aelf's architecture, which comprises the aelf chains, the AI oracle network, and AI applications, serving as the bridge and hub for integrating AI capabilities into the blockchain.
On-chain AI
Currently, the AI oracle field primarily focuses on ensuring the integrity of the AI computation process (such as ORA) by incorporating Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) at each step of the calculation and reasoning process. This approach ensures that the reasoning process is derived from the Large Language Model (LLM) itself, rather than human intervention. However, merely guaranteeing the integrity of the AI reasoning process is insufficient. It is also crucial to ensure that the higher-layer AI Agent application remains tamper-proof.
Additionally, widely used large models such as ChatGPT or decentralised computing networks like IO have their own computation and operation mechanisms, making it impractical to embed the ZKP process. Therefore, we believe that ensuring the integrity of the APIs called by the large model and the upper-layer AI Agent application is more critical and valuable than merely focusing on the AI inference process.
Implementation on aelf
aelf employs the following mechanisms to implement the AI oracle network:
- TLSNotary Mechanism: This ensures that the API provided by the underlying centralised or decentralised LLM remains untampered from the data source to the local endpoint.
- SGX and Decentralised Computing Networks: These technologies guarantee the trustworthy operation of AI agents.
The aelf oracle architecture is primarily divided into two components: 1. on-chain and 2. off-chain.
1. On-Chain Components
The on-chain components (currently on the aelf chain, with potential future deployment on Ethereum or other chains) include node pledge management, a reputation system, fee and income settlement, an AI Agent scheduler, and an AI Agent factory contract. These components form the foundational framework contracts for the AI oracle. Combined with off-chain nodes, they constitute the aelf oracle network. Specifically, the developer-defined AI oracle contract is generated by the AI Agent factory contract based on user-defined logic.
- Node Pledge Management: Manages the AI Agent Service Nodes. Any node joining the network must pledge a certain amount of ELF.
- Reputation System: Evaluates node operating status in conjunction with the committee's assessments, such as downgrading offline nodes.
- Cost and Revenue Settlement: Integrates with the AI Agent scheduler to settle revenue for nodes and charge fees for dApp calls.
- AI Agent Scheduler: Deploys and schedules AI Agent Service code based on network computing power load.
- AI Agent Factory: Generates custom contracts for any user-defined AI Agent logic. It acts as the intermediary between the foundational framework contract and the user-defined contract, forwarding the dApp call interface, and interacting with the fee and income settlement contract. Additionally, it mediates between the AI Agent Service and user-defined contracts, processing all calls and inference results of the AI Agent Services uniformly.
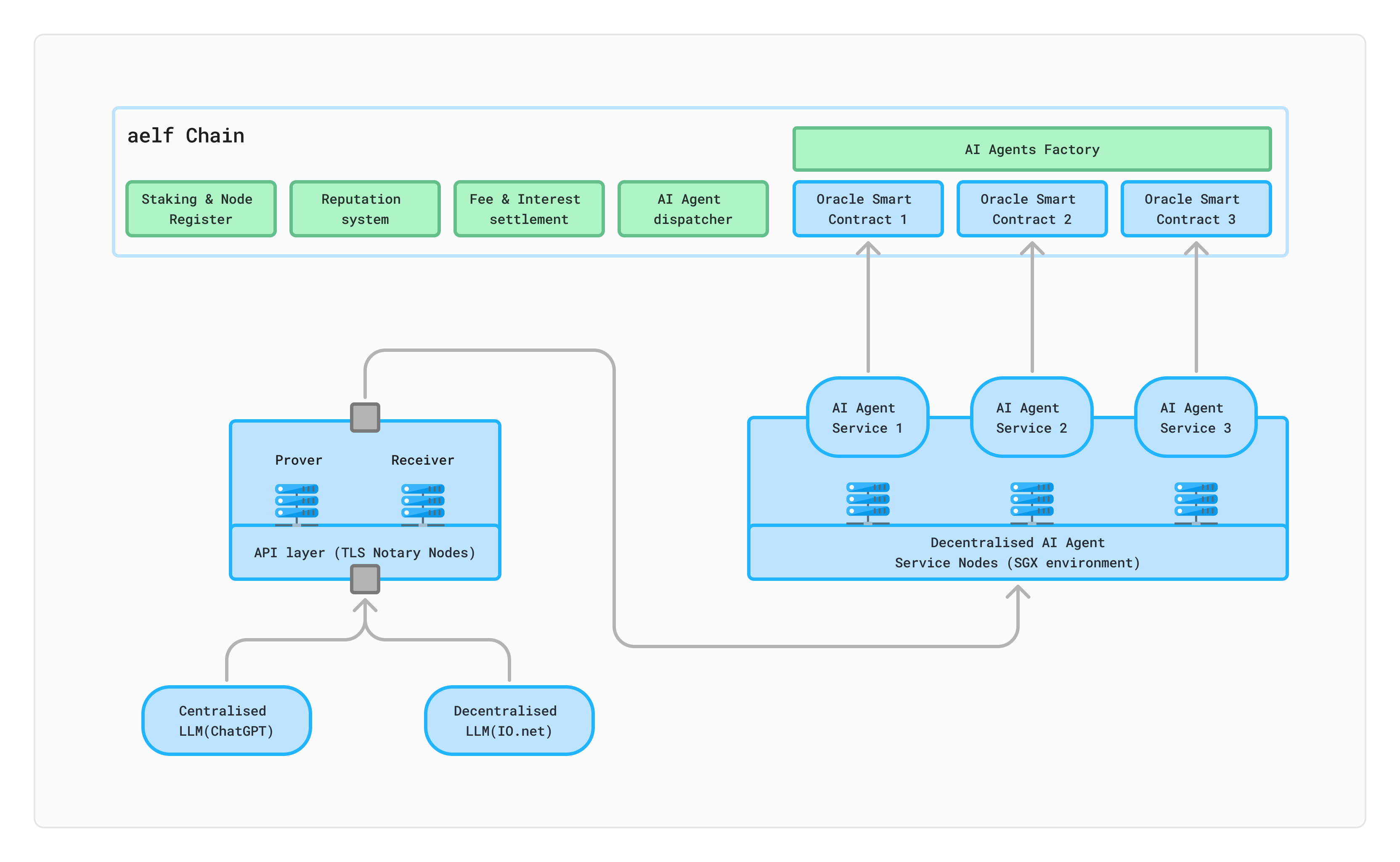
2. Off-Chain Components
The off-chain components consist of TLS Notary Nodes and Decentralised AI Agent Service Nodes (SGX environment).
TLS Notary Nodes
TLS Notary is an attestation mechanism that ensures the integrity and security of network communications between untrusted participants using the TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocol. This protocol encrypts communications between clients and servers. The "Notary" refers to a trusted third party or node that verifies the integrity of the TLS session between the client and server, ensuring it has not been tampered with. TLS Notary captures and records key information from the TLS session, such as the encrypted handshake and session keys, enabling even untrusted participants to verify the session's integrity. This mechanism allows the upper-layer AI Agent Service to authenticate data from external servers without fully trusting them. Evidence from TLS Notary can be used in the on-chain verification process to ensure the AI Agent Service processes safe and trustworthy data. aelf currently employs TLS Notary Nodes through two independent nodes: Receiver and Notary.
Decentralised AI Agent Service Nodes
The Decentralised AI Agent Service Nodes form a decentralised AI Agent computing network utilising Intel's SGX (Software Guard Extensions) technology. SGX creates a "trusted execution environment" at the processor level, providing secure and reliable data processing capabilities. In the aelf oracle network, the AI Agent Service operates within the SGX execution environment, ensuring that even node operators cannot access the details of the AI Agent Service execution. This SGX-based technology protects the security of AI Agent code operations from tampering, and when combined with blockchain technology, provides tamper-proof records and decentralised trust. Developers deploy and run their AI Agent Services on this secure layer of the aelf oracle network.
AI Oracle Use on aelf
aelf will provide a comprehensive SDK and framework and developers only need to develop custom core logic and configure the interaction interfaces. The framework can automatically generate, schedule, and deploy the relevant AI Agent Services to the oracle network, and trigger the AI Agent Factory to generate the associated AI smart contracts.
For simple AI call logic, this process is fully automated. However, for more complex AI Agent Services (the framework currently integrates with the ChatGPT API and can connect with additional LLMs in the future), such as memory and embeddings, developers will need to develop these services themselves using the provided interface documentation.
Additionally, the aelf AI Oracle offers traditional services such as price feeds and random number generation. Using the aelf AI Oracle SDK, developers can customise their code to create limitless on-chain AI application scenarios.
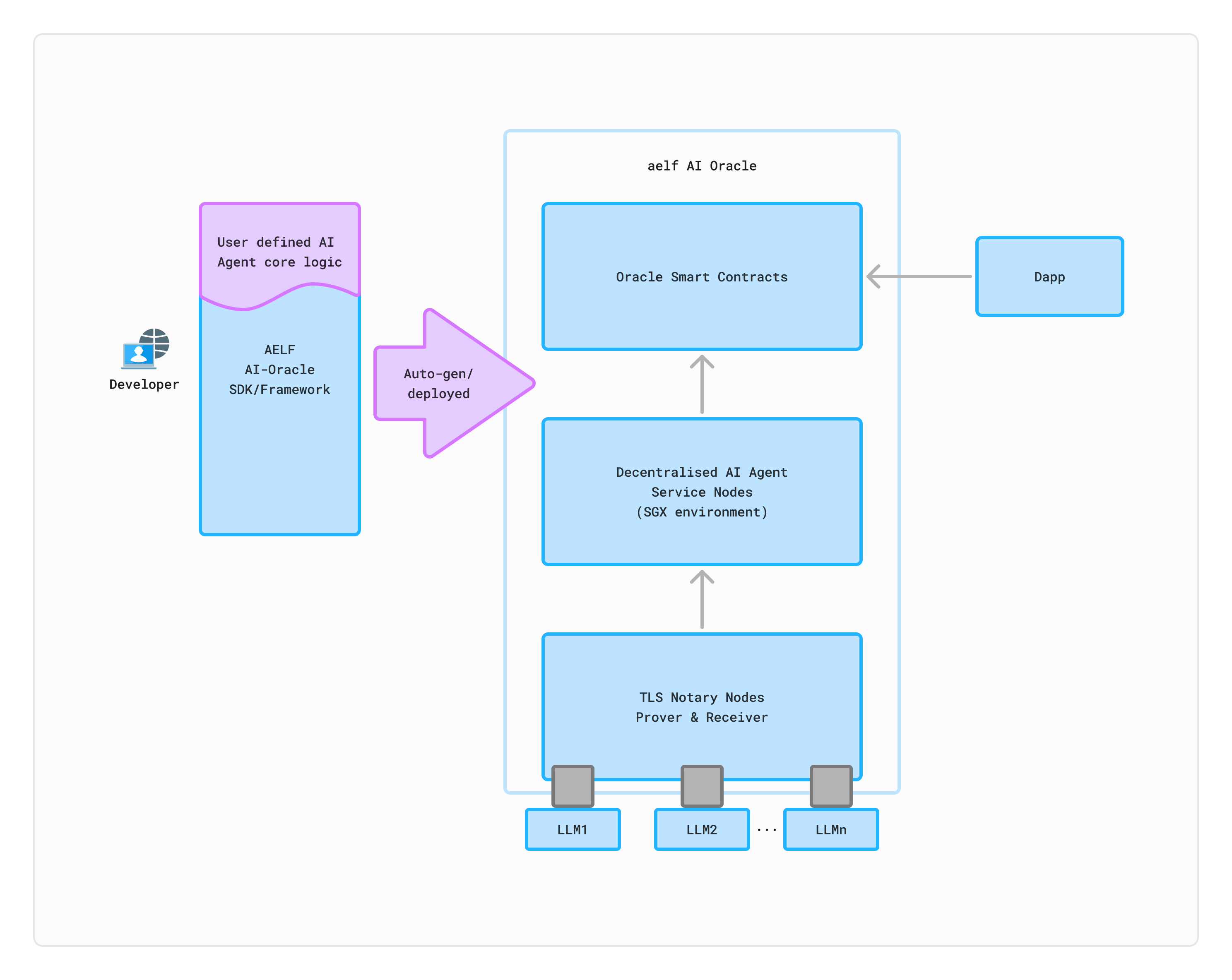
The aelf AI Oracle is committed to fostering the development of the AI Dapp ecosystem on aelf. This involves optimising the SDK and framework to enhance the interaction capabilities between AI Dapps and AI, as well as strengthening collaborations with AI Agent platforms. Currently, aelf AI Oracle will integrate with the ChatGPT API, and in the future, it plans to incorporate more centralised LLMs and collaborate with other decentralised AI computing networks to meet the growing needs of developers.
Beyond the aelf chain, aelf AI Oracle aims to expand to other major blockchains such as Ethereum, truly becoming the AI layer of Web3.
iii) Intelligent Load Balancing for aelf
Intelligent load balancing is a critical component for enhancing the scalability and performance of the aelf blockchain. By distributing the workload across the network more effectively, AI and machine learning can ensure that no single node becomes a bottleneck, thereby maintaining high transaction throughput and reducing latency.
Dynamic Traffic Distribution
Machine learning algorithms can analyse real-time network traffic and historical transaction patterns to dynamically distribute the workload. An AI model can predict which nodes are likely to become overloaded based on their current and past performance. By redirecting traffic away from these nodes to less utilised ones, the aelf network can prevent congestion and maintain smooth operations. A practical example of this outside of blockchain can be seen in content delivery networks such as Akamai and Cloudflare, which use AI to manage traffic distribution across global server networks. These systems continuously monitor server load, latency, and other metrics to ensure that content is delivered quickly and efficiently to users. Similarly, aelf intends to implement AI-driven load balancing to optimise transaction processing across its nodes.
Resource Utilisation Optimisation
AI can also optimise the use of network resources by balancing the computational load. This involves distributing smart contract execution and transaction validation tasks evenly across the network. Machine learning models can identify nodes with excess computational capacity and redirect tasks to these nodes, ensuring that all resources are utilised effectively. For example, Google's Borg system, which manages resources across its massive data centers, uses machine learning to allocate tasks dynamically based on available resources. This ensures high utilisation rates and minimises idle time. aelf is currently evaluating similar strategies to balance the workload across its network, ensuring that no single node is underutilised or overwhelmed.
Predictive Scaling
Predictive scaling is an important aspect of intelligent load balancing where AI models forecast future demand and scale resources accordingly. By analysing trends and patterns in transaction volumes, AI can predict when the network will experience high traffic and preemptively allocate additional resources to handle the load. This proactive approach ensures that the network remains responsive even during peak times. AWS Auto Scaling uses predictive algorithms to automatically adjust the number of active servers based on predicted load. This approach minimises response times and prevents service degradation. aelf leveraging similar predictive scaling techniques to ensure that its network can handle fluctuations in transaction volume without compromising performance.
Fault Tolerance and Redundancy
Intelligent load balancing also enhances fault tolerance and redundancy within the network. AI can monitor node health and performance, identifying and isolating nodes that exhibit signs of failure or degraded performance. By redirecting traffic away from these nodes and distributing it among healthy nodes, the network can maintain high availability and reliability. Systems like Netflix's Chaos Monkey, which intentionally induces failures in their infrastructure to test resilience, rely on intelligent load balancing to reroute traffic and maintain service continuity. aelf will be implementing similar AI-driven fault tolerance mechanisms to ensure that its network remains robust even in the face of individual node failures.
Intelligent load balancing, powered by AI and machine learning, offers substantial benefits for enhancing the scalability and performance of the aelf blockchain. By dynamically distributing traffic, optimising resource utilisation, enabling predictive scaling, and enhancing fault tolerance, AI-driven load balancing ensures that the aelf network can handle increasing transaction volumes efficiently.
iv) AI-Facilitated Cross-Chain Interoperability for aelf
Incorporating AI into aelf's cross-chain interoperability framework can significantly enhance the efficiency and security of data transfer and validation processes. By leveraging AI-driven optimisations, aelf can ensure seamless communication and robust performance within itself between MainChain and dAppChains, and more importantly with various other blockchain networks.
Optimising Data Transfer
AI will be instrumental in streamlining the data transfer process between the various blockchains connected to aelf. Machine learning algorithms can analyse historical data and current network conditions to predict optimal routing paths for data packets. This ensures that data is routed through the least congested and most efficient paths, reducing latency and improving transfer speeds. For instance, AI models can dynamically adjust routing paths based on real-time network traffic, similar to how AI optimises data flow in large-scale cloud computing networks used by companies like Google and Amazon. Furthermore, AI can employ predictive analytics to forecast network congestion and preemptively adjust data transfer protocols. This capability allows aelf to avoid potential bottlenecks and ensure that cross-chain transactions are processed efficiently. By continuously learning from network behaviour, AI algorithms can improve their predictions over time, leading to progressively better performance and reliability.
Enhanced Data Validation
AI can also enhance the security and accuracy of cross-chain transaction validation. Machine learning models, trained on vast datasets of transaction histories, can identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity or errors. AI-driven tools can flag transactions that deviate from typical behaviour, such as unusually large transfers or repeated transactions from the same node, which could indicate a security breach or double-spending attempt. aelf is working with several potential strategic partners to implement similar AI-driven validation mechanisms to ensure the integrity and security of cross-chain interactions.
v) AI-Driven Node Selection and Validation for aelf
As part of a longer-term initiative, our research team is currently in the exploratory phase of evaluating how AI might be incorporated into aelf's node selection and validation processes. This initiative, if pursued, can potentially significantly enhance both the speed and security of aelf consensus mechanisms.
Optimising Node Selection
Machine learning can be employed to analyse historical data and predict which nodes are most likely to perform reliably and securely. By evaluating factors such as past performance, network latency, and resource availability, AI models can prioritise nodes that are best suited for participating in the consensus process. For example, a neural network could be trained to predict node reliability based on metrics like uptime, transaction validation speed, and historical accuracy, ensuring that only the most capable nodes are selected for consensus.
One practical approach to achieving this involves the use of genetic algorithms, which are inspired by the process of natural selection. These algorithms can evolve optimal strategies for node selection by continuously iterating and improving based on predefined fitness criteria. For example, nodes that have demonstrated high reliability and low latency in past transactions are given higher priority, ensuring that the consensus process remains efficient and secure. This method has been effectively utilised in other domains, such as edge computing and task scheduling, to optimise resource allocation and performance.
Enhancing Consensus Security
AI can also enhance the security of the consensus process by dynamically adjusting the selection criteria based on real-time network conditions and potential threats. For instance, machine learning models can detect unusual patterns that might indicate a security threat, such as a potential Sybil attack where multiple nodes controlled by a single entity attempt to dominate the network. By identifying and mitigating these risks in real-time, AI ensures that the consensus mechanism remains robust and secure.
A specific implementation of this concept could involve anomaly detection algorithms. These algorithms can monitor network activity for deviations from normal behaviour, such as sudden spikes in node participation or unusual transaction patterns. When such anomalies are detected, the AI system can flag these nodes for further scrutiny or exclude them from the consensus process, thus protecting the network from potential attacks. This approach leverages AI's ability to process and analyse large volumes of data in real-time, providing a proactive security measure for the blockchain.
As node elections are fundamental to network consensus and security, we may integrate the aelf AI Oracle to ensure that the elections are open, transparent, and trustworthy.