ToDo dApp
Description: This contract is moderately complex, demonstrating task management functionalities such as creating, updating, and deleting tasks. It also includes features for task prioritization and user interaction.
Purpose: To introduce you to task management systems in smart contracts, focusing on state management, user interactions, and contract updates for efficient handling of to-do tasks.
Difficulty Level: Moderate
Step 1 - Setting up your development environment
- Local
- Codespaces
- Basic knowledge of terminal commands
- IDE - Install VS Code
Note for Apple Silicon users:
Ensure that Rosetta is installed, if it is not, use the following command:
softwareupdate --install-rosetta
Install Required Packages
- Install dotnet 8.0.x SDK
- Install aelf contract templates
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
dotnet new --install AElf.ContractTemplates
dotnet new install AElf.ContractTemplates
AELF.ContractTemplates contains various predefined templates for the ease of developing smart contracts on the aelf blockchain.
- Install aelf deploy tool
dotnet tool install --global aelf.deploy
aelf.deploy is a utility tool for deploying smart contracts on the aelf blockchain. Please remember to export PATH after installing aelf.deploy.
ℹ️ Note: If you have installed aelf.deploy and your terminal says that there is no such command available, please uninstall and install aelf.deploy.
Install Node.js and Yarn
Install aelf-command
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
sudo npm i -g aelf-command
npm i -g aelf-command
aelf-command is a CLI tool for interacting with the aelf blockchain, enabling tasks like creating wallets and managing transactions. Provide required permissions while installing aelf-command globally.
- Visit aelf-devcontainer-template.
- Click the
Use this templatebutton. ChooseCreate a new repository. - Enter a suitable repository name. Click
Create repository. - Within the GitHub interface of your new repository, click on
Code. SelectCodespaces. - Click on the
+sign to create a new Codespace. - After some time, your workspace will load with the contents of the repository. You can now continue your development using GitHub Codespaces.
Step 2 - Develop Smart Contract
Start Your Smart Contract Project
-
Open your
Terminal. -
Enter the following command to generate a new project:
mkdir todo-app
cd todo-app
dotnet new aelf -n ToDoApp
Adding Your Smart Contract Code
Now that we have a template todo list project, we can customise the template to incorporate our own contract logic. Let's start by implementing methods to handle the basic functionality of creating, editing, listing, deleting, and marking tasks as complete within the contract state. ToDo dApp includes the below functionalities like:
- Create a task (Name, category, description, createAt, updatedAt)
- Mark task as completed
- Delete a task
- List all the tasks
- Edit a task
- Enter this command in your
Terminal.
cd src
Defining Methods and Messages
- Rename the proto file name
hello_world_contract.protoinside folderProtobuf/contract/totodo_app.proto:
mv Protobuf/contract/hello_world_contract.proto Protobuf/contract/todo_app.proto
The .proto file defines the structure and serialization of data, ensuring consistent communication and data exchange between the contract and external systems.
- Open the project with your IDE.
The implementation of todo_app.proto file inside folder src/Protobuf/contract/ is as follows:
syntax = "proto3";
import "aelf/options.proto";
import "google/protobuf/empty.proto";
import "google/protobuf/wrappers.proto";
import "Protobuf/reference/acs12.proto";
// The namespace of this class
option csharp_namespace = "AElf.Contracts.ToDo";
service ToDo {
// The name of the state class the smart contract is going to use to access blockchain state
option (aelf.csharp_state) = "AElf.Contracts.ToDo.ToDoState";
option (aelf.base) = "Protobuf/reference/acs12.proto";
rpc Initialize (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
rpc CreateTask (TaskInput) returns (google.protobuf.StringValue) {
}
rpc UpdateTask (TaskUpdateInput) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
rpc DeleteTask (google.protobuf.StringValue) returns (google.protobuf.Empty) {
}
rpc ListTasks (google.protobuf.StringValue) returns (TaskList) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
rpc GetTask (google.protobuf.StringValue) returns (Task) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
rpc GetInitialStatus (google.protobuf.Empty) returns (google.protobuf.BoolValue) {
option (aelf.is_view) = true;
}
}
// A message to represent a task
message Task {
string task_id = 1;
string name = 2;
string description = 3;
string category = 4;
string status = 5;
string owner = 6;
int64 created_at = 7;
int64 updated_at = 8;
}
// Input for creating a task
message TaskInput {
string name = 1;
string description = 2;
string category = 3;
}
// Input for updating a task
message TaskUpdateInput {
string task_id = 1;
string name = 2;
string description = 3;
string category = 4;
string status = 5;
}
// List of tasks
message TaskList {
repeated Task tasks = 1;
}
rpcmethods define the callable functions within the contract, allowing external systems to interact with the contract's logic.messagerepresent the structured data exchanged between the contract and external systems.
Define Contract States
The implementation of the ToDo app state inside file src/ToDoAppState.cs is as follows:
using AElf.Sdk.CSharp.State;
using AElf.Types;
namespace AElf.Contracts.ToDo
{
public class ToDoState : ContractState
{
public BoolState Initialized { get; set; }
public SingletonState<Address> Owner { get; set; }
public MappedState<string, Task> Tasks { get; set; } // Mapping of task ID to Task
public MappedState<string, bool> TaskExistence { get; set; } // Mapping to track task existence
public StringState TaskIds { get; set; } // Concatenated string of task IDs
public Int32State TaskCounter { get; set; } // Counter for generating unique IDs
}
}
- The
State.csfile in an aelf blockchain smart contract holds the variables that store the contract's data, making sure this data is saved and accessible whenever the contract needs it.
Implement ToDo Smart Contract
The implementation of the ToDo App smart contract inside file src/ToDoApp.cs is as follows:
using Google.Protobuf.WellKnownTypes;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace AElf.Contracts.ToDo
{
public class ToDo : ToDoContainer.ToDoBase
{
public override Empty Initialize(Empty input)
{
if (State.Initialized.Value)
{
return new Empty();
}
State.Initialized.Value = true;
State.Owner.Value = Context.Sender;
State.TaskIds.Value = "";
State.TaskCounter.Value = 0;
return new Empty();
}
public override StringValue CreateTask(TaskInput input)
{
if (!State.Initialized.Value)
{
return new StringValue { Value = "Contract not initialized." };
}
var taskId = (State.TaskCounter.Value + 1).ToString();
State.TaskCounter.Value++;
var timestamp = Context.CurrentBlockTime.Seconds;
// Create task dictionary entry directly in ToDo class
State.Tasks[taskId] = new Task
{
TaskId = taskId,
Name = input.Name,
Description = input.Description,
Category = input.Category,
Status = "pending",
CreatedAt = timestamp,
UpdatedAt = timestamp,
Owner = Context.Sender.ToString().Trim('"'),
};
State.TaskExistence[taskId] = true;
// Append task ID to the list of IDs
var existingTaskIds = State.TaskIds.Value;
existingTaskIds += string.IsNullOrEmpty(existingTaskIds) ? taskId : $",{taskId}";
State.TaskIds.Value = existingTaskIds;
return new StringValue { Value = taskId };
}
public override Empty UpdateTask(TaskUpdateInput input)
{
var task = State.Tasks[input.TaskId];
if (task == null)
{
return new Empty(); // Handle case if task doesn't exist
}
task.Name = input.Name ?? task.Name;
task.Description = input.Description ?? task.Description;
task.Category = input.Category ?? task.Category;
task.Status = input.Status ?? task.Status;
task.UpdatedAt = Context.CurrentBlockTime.Seconds;
State.Tasks[input.TaskId] = task;
return new Empty();
}
public override Empty DeleteTask(StringValue input)
{
State.Tasks.Remove(input.Value);
State.TaskExistence.Remove(input.Value);
// Remove task ID from the list of IDs
var existingTaskIds = State.TaskIds.Value.Split(',');
var newTaskIds = new List<string>(existingTaskIds.Length);
foreach (var taskId in existingTaskIds)
{
if (taskId != input.Value)
{
newTaskIds.Add(taskId);
}
}
State.TaskIds.Value = string.Join(",", newTaskIds);
return new Empty();
}
public override TaskList ListTasks(StringValue input)
{
var owner = input.Value; // Get the owner value from the input
var taskList = new TaskList();
var taskIds = State.TaskIds.Value.Split(',');
foreach (var taskId in taskIds)
{
var task = State.Tasks[taskId];
if (task != null && task.Owner == owner) // Filter tasks by owner
{
taskList.Tasks.Add(task);
}
}
return taskList;
}
public override Task GetTask(StringValue input)
{
var task = State.Tasks[input.Value];
if (task == null)
{
return new Task { TaskId = input.Value, Name = "Task not found." };
}
return task;
}
public override BoolValue GetInitialStatus(Empty input)
{
return new BoolValue { Value = State.Initialized.Value };
}
}
}
Building Smart Contract
- Build the smart contract code with the following command inside
srcfolder:
dotnet build
You should see ToDoApp.dll.patched in the directory ToDoApp/src/bin/Debug/net.6.0
Step 3 - Deploy Smart Contract
Create A Wallet
To send transactions on the aelf blockchain, you must have a wallet.
- Run this command to create aelf wallet.
aelf-command create

- You will be prompted to save your account, please do save your account as shown below:
? Save account info into a file? (Y/n) Y
Make sure to choose Y to save your account information.
ℹ️ Note: If you do not save your account information (by selecting n or N), do not export the wallet password. Only proceed to the next step if you have saved your account information.
- Next, enter and confirm your password. Then export your wallet password as shown below:
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
export WALLET_PASSWORD="YOUR_WALLET_PASSWORD"
$env:WALLET_PASSWORD = "YOUR_WALLET_PASSWORD"
Acquire Testnet Tokens (Faucet) for Development
To deploy smart contracts or execute on-chain transactions on aelf, you'll require testnet ELF tokens.
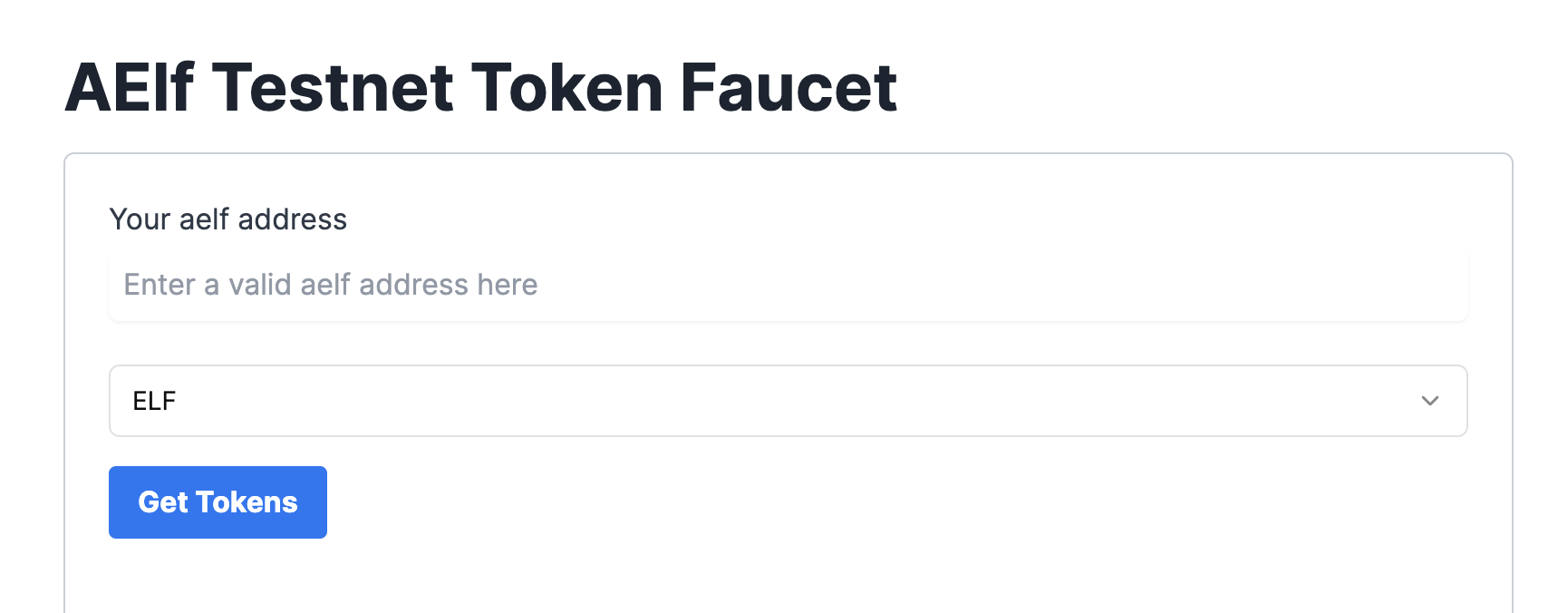
Get ELF Tokens
Go to https://faucet-ui.aelf.dev Enter your address and click Get Tokens.
Deploy Smart Contract:
The smart contract needs to be deployed on the chain before users can interact with it.
Run the following command to deploy a contract. Remember to export the path of ToDoApp.dll.patched to CONTRACT_PATH.
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
export CONTRACT_PATH=$(find ~+ . -path "*patched*" | head -n 1)
aelf-deploy -a $WALLET_ADDRESS -p $WALLET_PASSWORD -c $CONTRACT_PATH -e https://tdvw-test-node.aelf.io/
$CONTRACT_PATH = Get-ChildItem -Recurse -Filter "*patched*" | Select-Object -First 1 -ExpandProperty FullName
$env:CONTRACT_PATH = $CONTRACT_PATH
aelf-deploy -a $env:WALLET_ADDRESS -p $env:WALLET_PASSWORD -c $env:CONTRACT_PATH -e https://tdvw-test-node.aelf.io/
-
Please wait for approximately 1 to 2 minutes. If the deployment is successful, it will provide you with the contract address.
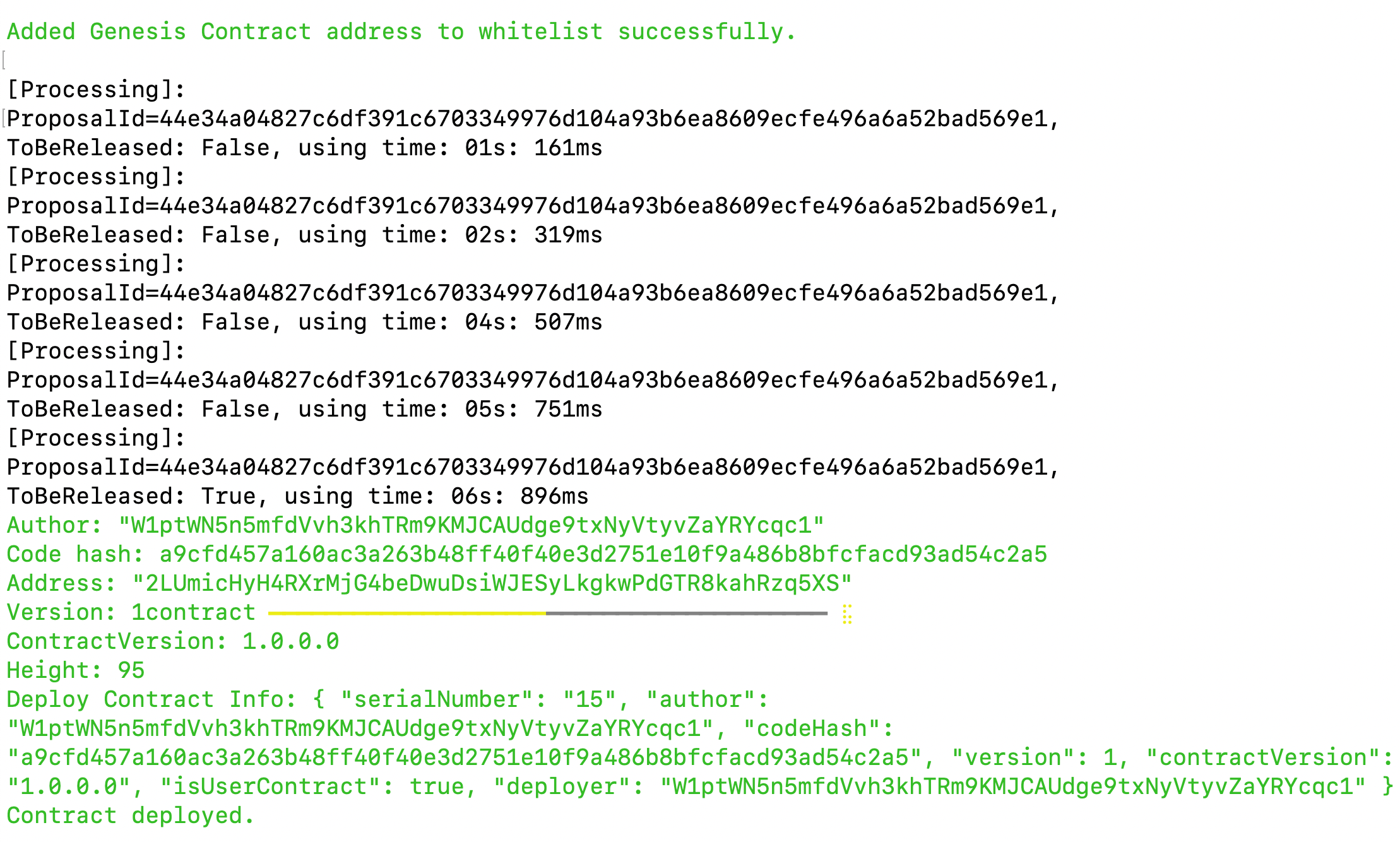
-
Copy the smart contract address from the
addressfield
-
Export your smart contract address:
- Linux and macOs
- Windows
export CONTRACT_ADDRESS="YOUR_SMART_CONTRACT_ADDRESS e.g. 2LUmicHyH4RXrMjG4beDwuDsiWJESyLkgkwPdGTR8kahRzq5XS"
$env:CONTRACT_ADDRESS="YOUR_SMART_CONTRACT_ADDRESS e.g. 2LUmicHyH4RXrMjG4beDwuDsiWJESyLkgkwPdGTR8kahRzq5XS"
ℹ️ Note: You are to copy the smart contract address as we will be referencing it in the next steps!
🎉 You have successfully deployed your ToDo dApp smart contract on the aelf testnet! In the next steps, we will be building the frontend components that allow us to interact with our deployed smart contract!
Step 4 - Interact with Your Deployed Smart Contract through dApp
Project Setup
Let's start by cloning the frontend project repository from github.
git clone https://github.com/AElfProject/aelf-samples.git
- Next, navigate to the frontend project directory with this command:
cd aelf-samples/todo/2-dapp
- Once you're inside the
2-dappdirectory, open the project with your preferred IDE (e.g., VSCode). You should see the project structure as shown below.
Install necessary libraries
- Run this command in the terminal to install all necessary packages and libraries:
npm install
We are now ready to build the frontend components of our ToDo dApp.
Configure Portkey Provider & Write Connect Wallet Function
Now, we'll set up our Portkey wallet provider to allow users to connect their Portkey wallets to the dApp and interact with the smart contract. We'll be interacting with the already deployed ToDo smart contract for this tutorial.
Step 1. Locate the File:
- Go to the
src/hooks/useTodoSmartContract.tsfile.
Step 2. Fetch the Smart Contract:
-
Find the comment
//Step A - Function to fetch a smart contract based on deployed wallet address -
Replace the existing
fetchContractfunction with this updated code:
//Step A - Function to fetch a smart contract based on deployed wallet address
const fetchContract = async () => {
if (!provider) return null;
try {
// 1. get the dAppChain tDVW using provider.getChain
const chain = await provider?.getChain("tDVW");
if (!chain) throw new Error("No chain");
//Address of ToDo Smart Contract
//Replace with Address of Deployed Smart Contract
const address = "your_deployed_todo_contract_address";
// 2. get the ToDo contract
const todoContract = chain?.getContract(address);
setSmartContract(todoContract);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error, "====error");
}
}
ℹ️ Note: You are to replace the address placeholder with your deployed ToDo smart contract address from "Deploy Smart Contract" step!
example: //Replace with Address of Deployed Smart Contract const address = "your_deployed_todo__smart_contract_address";
Explanation:
-
fetchContractFunction: This function fetches a smart contract based on the given chain symbol (e.g., "AELF" or "tDVW") and the contract address.- Check Provider : If no provider is available, the function returns null.
- Fetch Chain : The function fetches chain information using the provider.
- Get Contract : It retrieves the smart contract instance from the chain.
AELF represents the mainnet chain and tDVW represents the testnet chain respectively on aelf blockchain.
Step 3. Initialize and Fetch the Smart Contracts:
-
Find the comment
// Step B - Effect hook to initialize and fetch the smart contract when the provider changes. -
Replace the existing
useEffecthook with this updated code:
// Step B - Effect hook to initialize and fetch the smart contract when the provider changes
useEffect(() => {
fetchContract();
}, [provider]); // Dependency array ensures this runs when the provider changes
Explanation:
useEffectHook : This hook initializes and fetches the smart contracts when the provider changes.- Check Provider : If no provider is available, the function returns null.
- Fetch Contracts : It fetches and sets the smart contracts.
By following these steps, we'll configure the Portkey provider to connect users' wallets to our app and interact with the ToDo smart contract including task management related functionalities. This setup will enable our frontend components to perform actions like Create Task, Edit Task, and Delete Task.
Configure Connect Wallet Function
Step 1: Locate the File
- Go to the
src/components/layout/header/index.tsxfile.
Step 2: Write the Connect Wallet Function
-
The
header/index.tsxfile is the header of our ToDo dApp. It allows users to connect their Portkey wallet with the ToDo dApp. -
Before users can interact with the smart contract, we need to write the
Connect Walletfunction. -
Find the comment
// Step C - Connect Portkey Wallet. -
Replace the existing connect function with this code snippet:
const connect = async (walletProvider?: IPortkeyProvider) => {
// Step C - Connect Portkey Wallet
const accounts = await (walletProvider ? walletProvider : provider)?.request({
method: MethodsBase.REQUEST_ACCOUNTS,
});
const account = accounts?.AELF && accounts?.AELF[0];
if (account) {
setCurrentWalletAddress(account.replace(/^ELF_/, "").replace(/_AELF$/, ""));
setIsConnected(true);
}
!walletProvider && toast.success("Successfully connected");
};
Explanation:
connectFunction : This function connects the user's Portkey wallet with the dApp.- Fetch Accounts : It fetches the wallet accounts using the provider.
- Log Accounts : Logs the accounts to the console for debugging.
- Set Wallet Address : Sets the current wallet address state variable with the fetched account.
- Update Connection Status : Updates the state to indicate that the wallet is connected.
- User Notification : Displays an alert to notify the user that their wallet is successfully connected.
In this code, we fetch the Portkey wallet account using the provider and update the wallet address state variable. An alert notifies the user that their wallet is successfully connected.
With the connect wallet function defined, we're ready to write the remaining functions in the next steps.
Configure Create Task Form
Step 1: Locate the File
- Go to the
src/pages/home/index.tsxfile. This file contains all the functionalities like show user's Task, CreateTask, UpdateTask, DeleteTask and Filter all Tasks, etc.
Step 2: Prepare Form to Create and Update Tasks
-
Find the comment
// Step D - Configure Todo Form. -
Replace the form variable with this code snippet:
// Step D - Configure Todo Form
const form = useForm<z.infer<typeof formSchema>>({
resolver: zodResolver(formSchema),
defaultValues: {
name: "",
description: "",
},
});
Here's what the function does:
-
Initializes a new form variable with default values needed to create a task.
-
Fields include:
nameanddescription.
Now the form is ready for users to fill in the necessary details.
Check Contract Initialization
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// step 1 - Check if contract is initialized or not. -
Replace the existing
checkIsContractInitializedfunction with this code snippet:
// step 1 - Check if contract is initialized or not
const checkIsContractInitialized = async () => {
const result = await smartContract?.callViewMethod("GetInitialStatus", ""); // Call the GetInitialStatus method which is present on Smart Contract
setIsContractInitialized(result?.data?.value); // Expect value True if it's Initialized otherwise NULL if it's not
};
Initialize Contract
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// step 2 - Initialize the smart contract. -
Replace the existing
initializeContractfunction with this code snippet:
// step 2 - Initialize the smart contract
const initializeContract = async () => {
let initializeLoadingId;
try {
// Start Loading
initializeLoadingId = toast.loading("Initializing a Contract..");
await smartContract?.callSendMethod(
"Initialize", // Function Name
currentWalletAddress as string, // User Wallet Address
{} // No Arguments
);
// Update Loading Message with Success
toast.update(initializeLoadingId, {
render: "Contract Successfully Initialized",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
} catch (error: any) {
// Update Loading Message with Error
toast.update(initializeLoadingId as Id, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
} finally {
// Remove Loading Message
removeNotification(initializeLoadingId as Id);
}
};
Create a New Task
-
Write the function to
Create a New Task** -
The
home/index.tsxfile includes the code to create tasks. It allows users to create new tasks. -
Find the comment
// step 3 - Create a New Task using Smart Contract. -
Replace the existing
createNewTaskfunction with this code snippet:
// step 3 - Create a New Task using Smart Contract
const createNewTask = async (values: {
name: string;
description: string;
}) => {
let createLoadingId;
try {
// Start Loading
createLoadingId = toast.loading("Creating a New Task..");
setFormLoading(true);
// Prepare Arguments for Create a New Task
const sendData = {
name: values.name,
description: values.description,
category: selectedCategory?.value,
status: TASK_STATUS.pending,
};
// Call CreateTask Function of Smart Contract
await smartContract?.callSendMethod(
"CreateTask",
currentWalletAddress as string,
sendData
);
// Update Loading Message with Success
toast.update(createLoadingId, {
render: "New Task Successfully Created",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
// Get New Data from Contract
getTodoData();
} catch (error: any) {
// Update Loading Message with Error
toast.update(createLoadingId as Id, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
} finally {
// Close Form Modal
handleCloseModal();
// Remove Loading Message
removeNotification(createLoadingId as Id);
setFormLoading(false);
}
};
What This Function Does:
-
Creates an Object with Task Details : It prepares the data needed to create a new task.
-
Calls Smart Contract Method : It interacts with the blockchain smart contract to create the new task using the prepared data.
Next, we'll write the Update an Existing Task function.
Update an Existing Task
Write the function for update an existing task.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// step 4 - Update an Existing Task. -
Replace the existing
updateTaskfunction with this code snippet:
// step 4 - Update an Existing Task
const updateTask = async (values: { name: string; description: string }) => {
let updateLoadingId;
try {
// Start Loading
updateLoadingId = toast.loading("Updating a Task..");
setFormLoading(true);
// Prepare Arguments for Update the Task
const sendData = {
taskId: updateId,
name: values.name,
description: values.description,
category: selectedCategory?.value,
status: TASK_STATUS.pending,
};
// Call UpdateTask Function of Smart Contract
await smartContract?.callSendMethod(
"UpdateTask",
currentWalletAddress as string,
sendData
);
// Update Loading Message with Success
toast.update(updateLoadingId, {
render: "Task Successfully Updated",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
// Get New Data from Contract
getTodoData();
} catch (error: any) {
// Update Loading Message with Error
toast.update(updateLoadingId as Id, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
} finally {
// Close Form Modal
handleCloseModal();
// Remove Loading Message
removeNotification(updateLoadingId as Id);
setFormLoading(false);
}
};
What This Function Does:
-
Creates an Object with Updated Task Details : It prepares the data needed for the updated task details
-
Calls Smart Contract Method : It interacts with the blockchain smart contract to update the existing task using the prepared data.
Next, we'll write the Update Task Status (completeTask) function.
Update the Task Status
Write the Function to update the task status (completeTask).
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// step 5- Update Status from Pending to Completed of the Task. -
Replace the existing
completeTaskfunction with the following code snippet:
// step 5- Update Status from Pending to Completed of the Task
const completeTask = async (data: ITodoObject) => {
let completeLoadingId;
try {
// Start Loading
completeLoadingId = toast.loading("Moving to Completed Task..");
setUpdateId(data.taskId); // set Update Id for Loading on Button
// Call UpdateTask Function of Smart Contract
await smartContract?.callSendMethod(
"UpdateTask",
currentWalletAddress as string,
{ ...data, status: TASK_STATUS.completed }
);
// Update Loading Message with Success
toast.update(completeLoadingId, {
render: "Task Moved to Completed",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
// Get New Data from Contract
await getTodoData();
} catch (error: any) {
// Update Loading Message with Error
toast.update(completeLoadingId as Id, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
} finally {
setUpdateId(null);
// Remove Loading Message
removeNotification(completeLoadingId as Id);
}
};
What This Function Does:
- Calls Smart Contract Method : It interacts with the blockchain smart contract to update the task status by passind the
completedstatus as an argument.
Next, we'll write the Delete the Task function.
Delete the Task
Write a function to delete an existing task.
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// step 6 - Delete the Task. -
Replace the existing
deleteTaskfunction with this code snippet:
// step 6 - Delete the Task
const deleteTask = async (data: ITodoObject) => {
let deleteLoadingId;
try {
// Start Loading
deleteLoadingId = toast.loading("Removing a Task..");
setDeletingId(data.taskId); // set Deleting Id for Loading on Button
// Call UpdateTask Function of Smart Contract and update the status as "Removed"
await smartContract?.callSendMethod(
"UpdateTask",
currentWalletAddress as string,
{ ...data, status: TASK_STATUS.removed }
);
// Update Loading Message with Success
toast.update(deleteLoadingId, {
render: "Task Successfully Removed",
type: "success",
isLoading: false,
});
// Get New Data from Contract
await getTodoData();
} catch (error: any) {
// Update Loading Message with Error
toast.update(deleteLoadingId as Id, {
render: error.message,
type: "error",
isLoading: false,
});
} finally {
setDeletingId(null);
// Remove Loading Message
removeNotification(deleteLoadingId as Id);
}
};
What This Function Does:
- Calls Smart Contract Method : It interacts with the blockchain smart contract to delete the existing task by passing status as "removed".
Next, we'll write the Handle Submit Form function.
Configure Submit Form
-
Scroll down to find the comment
// step 7 - Handle Submit Form. -
Replace the existing
onSubmitfunction with this code snippet:
// step 7 - Handle Submit Form
const onSubmit = async (values: { name: string; description: string }) => {
// Check Whether Contract Initialized or not
if (isContractInitialized !== true) {
await initializeContract(); // initialize the contract if it's not initialized before
}
// Check Whether Form is for Create or Update the Task
if (!!updateId) {
await updateTask(values); // Call updateTask for Update the task
} else {
await createNewTask(values); // Call createNewTask for Create a new task
}
};
What This Function Does:
-
Check initialized contract: It checks whether the smart contract is initialized or not by using
initializeContractfunction. -
Update Task: Call the
updateTaskfunction if updatedId has any value. -
Create Task: Call the
createNewTaskfunction if updatedId does not have any value.
Here, we have completed functions to Create Task, Update Task and Delete Task and now it's time to write a function to Fetch Tasks from the smart contract.
Fetch All Tasks
-
Scroll up to find the comment
// step 8 - Fetch All Tasks. -
Replace the existing
getTodoDatafunction with this code snippet:
// step 8 - Fetch All Tasks
const getTodoData = async () => {
try {
const result = await smartContract?.callViewMethod("ListTasks", {
value: currentWalletAddress,
});
console.log("result", result?.data);
setTodoData(result?.data ? result?.data.tasks : []);
} catch (error) {
console.log("error======", error);
} finally {
setLoading(false);
}
};
Here's what the function does:
- Fetches Task Data: It calls
ListTasksto get the list of all ToDo tasks from the ToDo smart contract. - Set Tasks on State: Get the result data from the smart contract and set an array of all tasks into
todoDataState.
We have prepared necessary function to fetch all the tasks created from a connected user's wallet.
Now that we've written all the necessary frontend functions and components, we're ready to run the ToDo dApp application in the next step.
Run Application
In this step, we will run the ToDo dApp application.
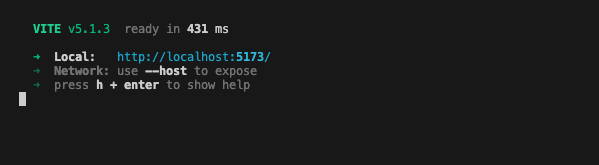
- To begin, run the following command on your terminal.
npm run dev
Note: Ensure that you are running this command under the todo/2-dapp folder.
-
You should observe the following as shown below.
-
Upon clicking on the localhost URL, you should be directed to the ToDo dApp landing page as shown below.
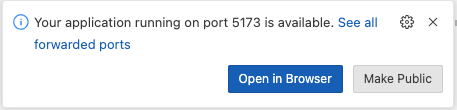
If you are developing and testing this with github codespace, you can use port forward to test the web server that is running in codespace, here is the link on how to use port forward for codespace https://docs.github.com/en/codespaces/developing-in-a-codespace/forwarding-ports-in-your-codespace
-
Usually codespace will automatically forward port, you should see a pop-up message at the bottom right of your codespace browser window as shown in the diagram below:
-
Click the link to open the ToDo dApp in the browser.
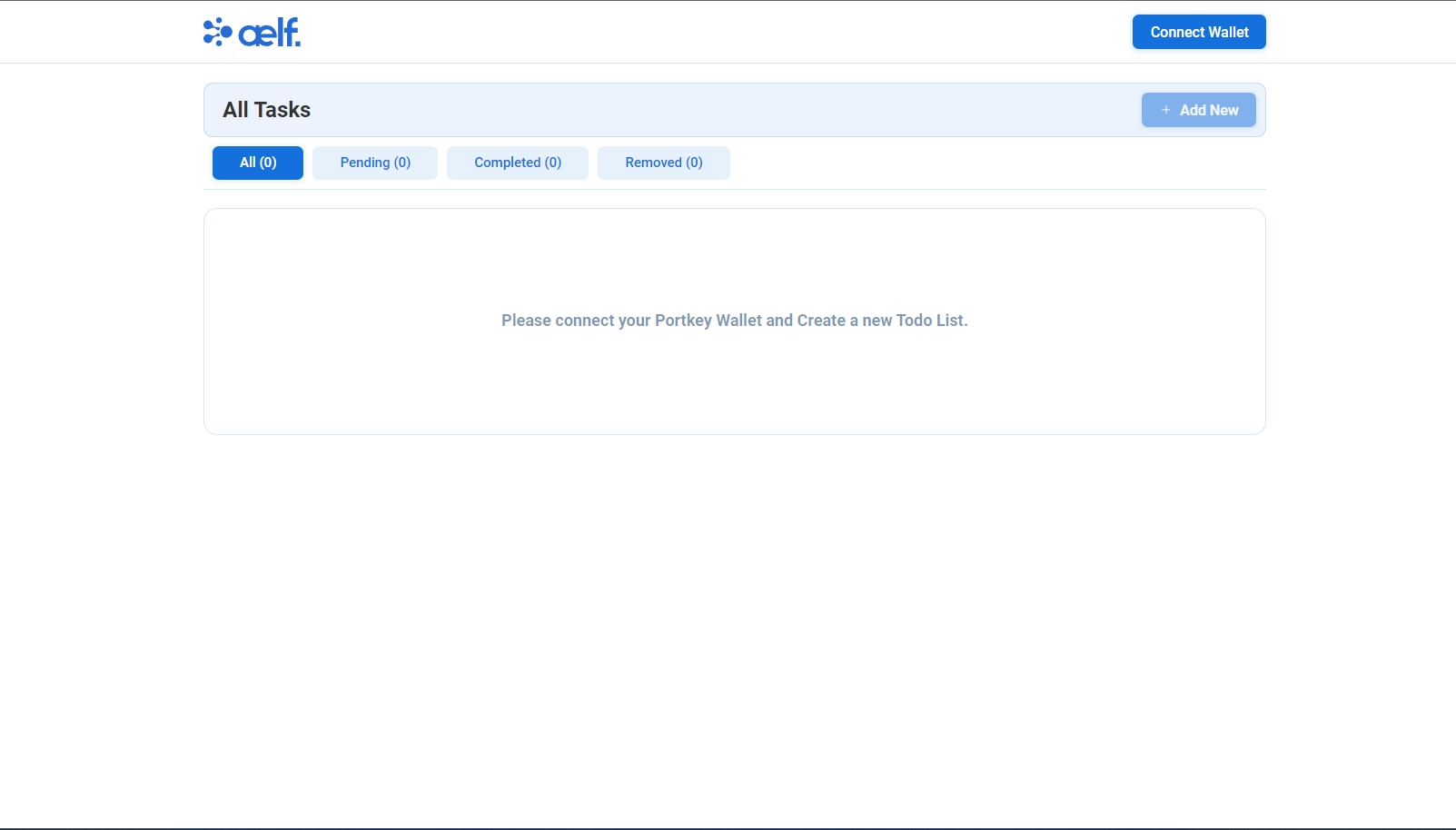
Create Portkey Wallet
Portkey is the first AA wallet from aelf's ecosystem, migrating users, developers and projects from Web2 to Web3 with DID solution.
Users can swiftly log into Portkey via their Web2 social info with no private keys or mnemonics required. Underpinned by social recovery and decentralized guardian design, Portkey safeguards users' assets from centralized control and theft. Portkey has a unique payment delegation mechanism which enables interested parties to function as delegatees to pay for user activities on users' behalf. This means that users can create accounts for free and fees for other usages may also be covered in Portkey.
Portkey also provides crypto on/off-ramp services, allowing users to exchange fiat with crypto freely. It supports the storage and management of various digital assets such as tokens, NFTs, etc. The compatibility with multi-chains and seamless connection to all kinds of DApps makes Portkey a great way to enter the world of Web3.
With DID solution as its core, Portkey provides both Portkey Wallet and Portkey SDKs.
For more information, you may visit the official documentation for Portkey at https://doc.portkey.finance/.
- Download the Chrome extension for Portkey from https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/portkey-wallet/iglbgmakmggfkoidiagnhknlndljlolb.
The Portkey extension supports Chrome browser only (for now). Please ensure that you are using Chrome browser. You may download Chrome from https://www.google.com/intl/en_sg/chrome/.
-
Once you have downloaded the extension, you should see the following on your browser as shown below.

-
Click on
Get Startand you should see the following interface as shown below.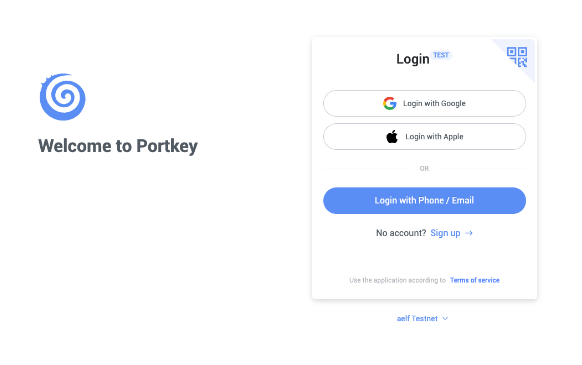
Sign up
-
Switch to aelf Testnet network by selecting it:
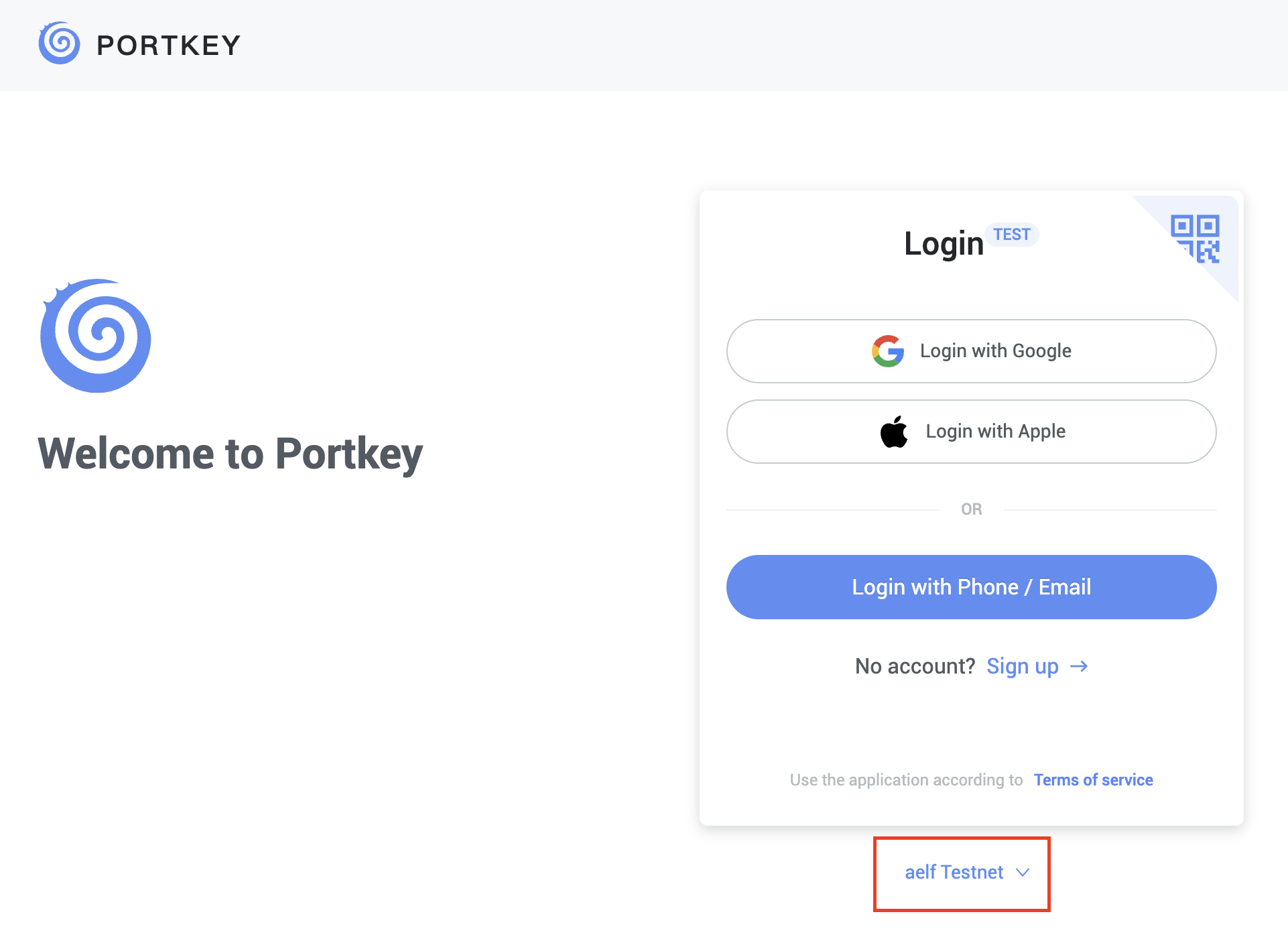
Please make sure you are using aelf Testnet in order to be able to receive your testnet tokens from the Faucet.
-
Proceed to sign up with a Google Account or your preferred login method and complete the necessary accounts creation prompts and you should observe the following interface once you have signed up.
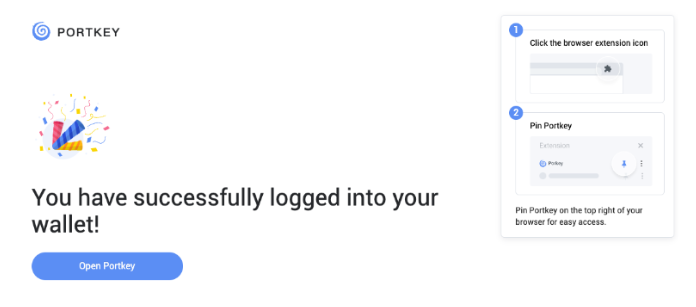
With that, you have successfully created your very first Portkey wallet within seconds. How easy was that?
It is highly recommended to pin the Portkey wallet extension for easier access and navigation to your Portkey wallet!
-
Next, click on ‘Open Portkey’ and you should now observe the following as shown below.
Connect Portkey Wallet
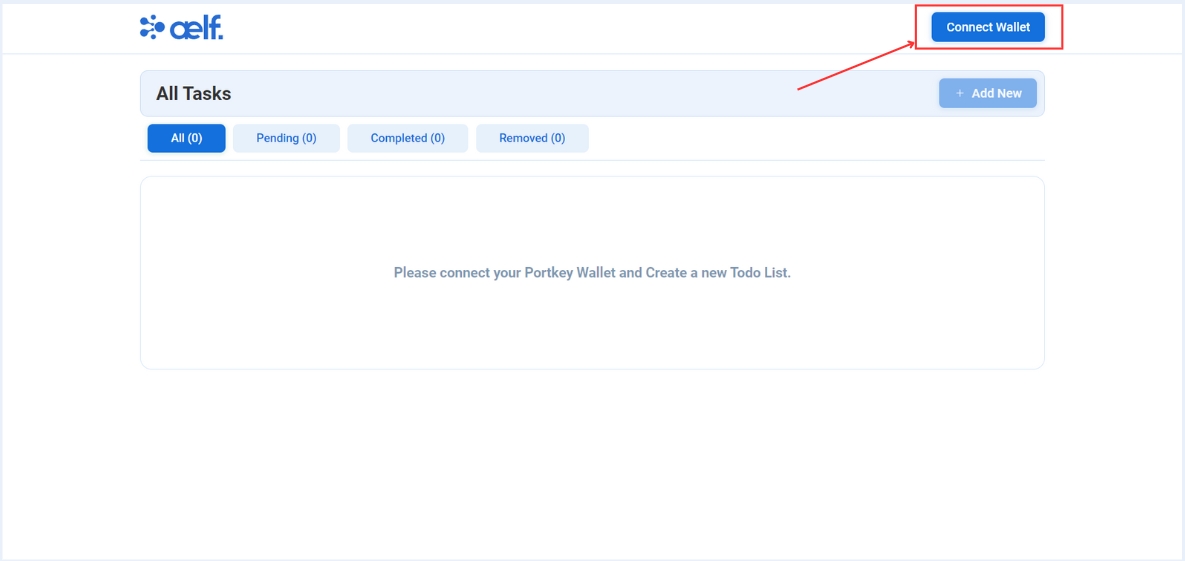
-
Click on "Connect Wallet" to connect your Portkey wallet.
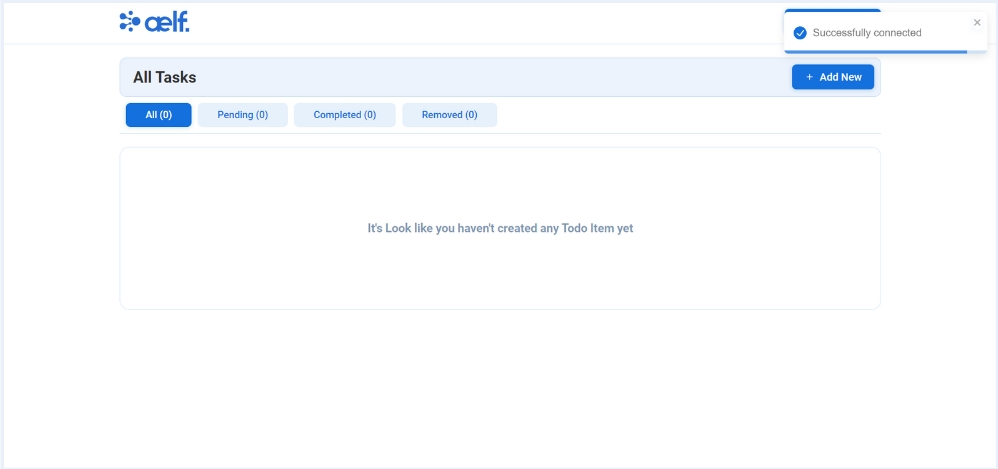
-
The button will change to "Your Wallet Address" when the connection is successful.
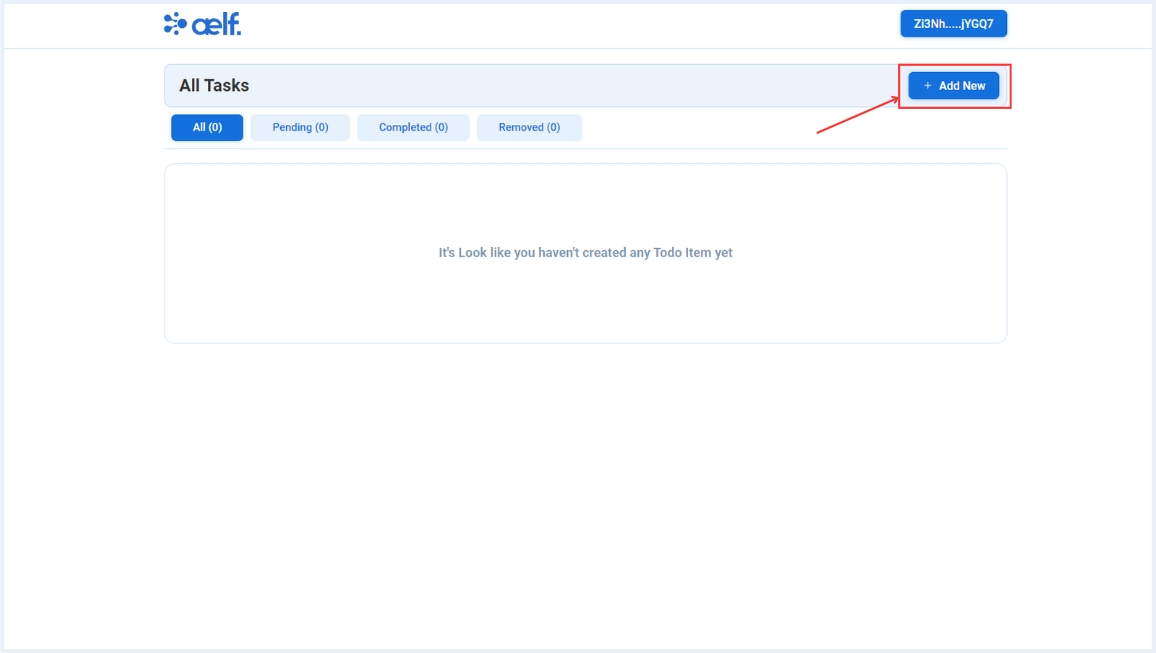
Create a New Task
-
Click on "Add New" button to create a new task.
-
You will see the pop-up modal with form to create a new task. Please fill all the necessary fields like
Name,DescriptionandCategory.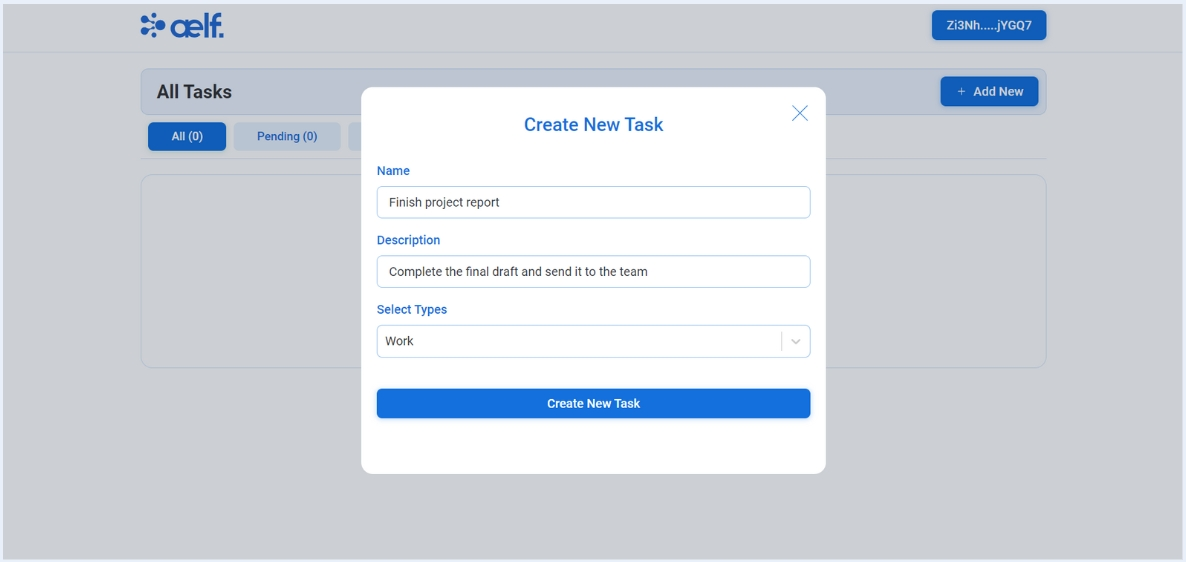
-
Click on Create New Task Button.
-
Now, You will receive a transaction request on your portkey wallet to Sign the transaction.
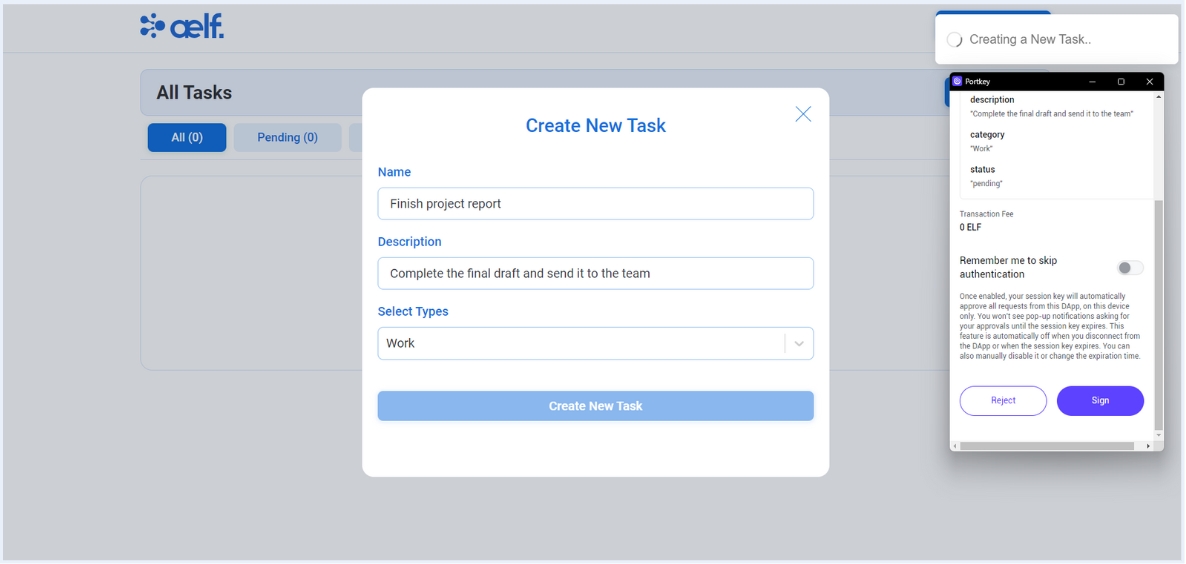
-
Click on Sign the transaction.
-
After the transaction is successfully processed, your first task will be created✅.
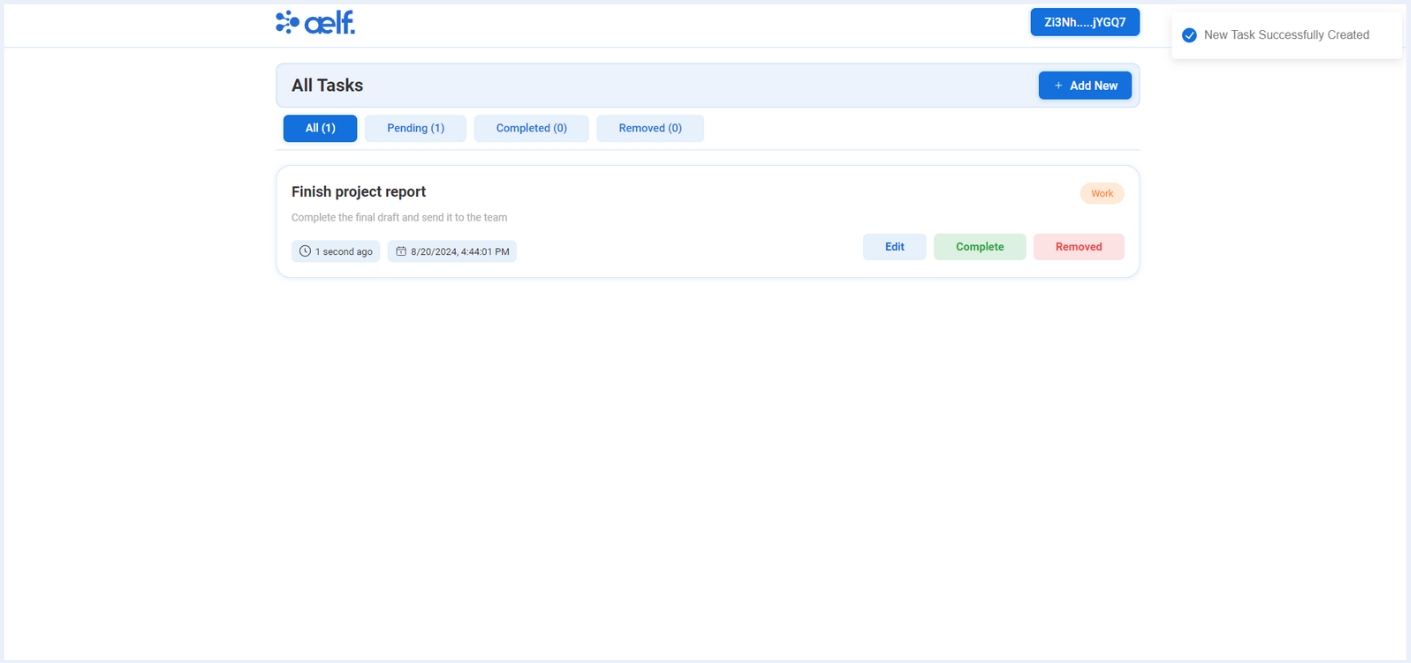
-
Your task item looks like below with the following details -
Name,Description,Last Updated Time,Create Date and Time,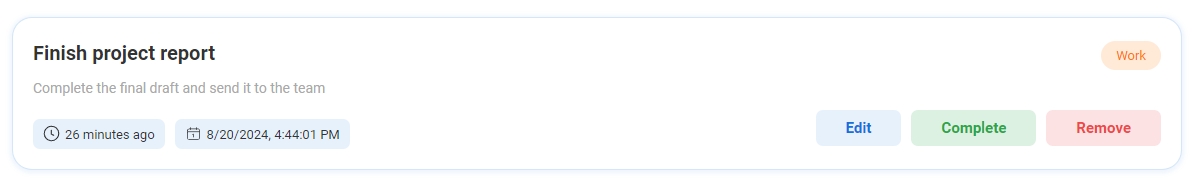
-
You will be able to perform these following action for a selected task -
Edit,Complete, andRemove.
As we have Created a Task successfully, let's update the task details.
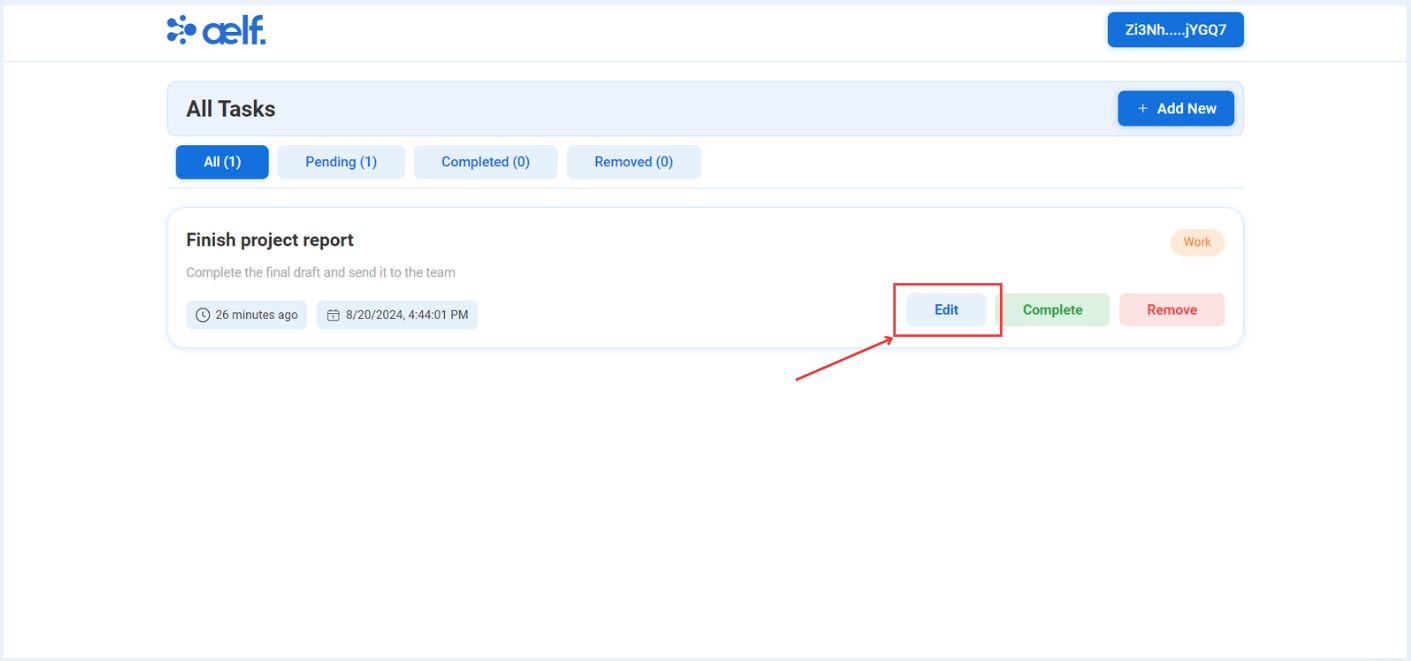
Edit the Task
-
Click on the "Edit" button to edit the task.
-
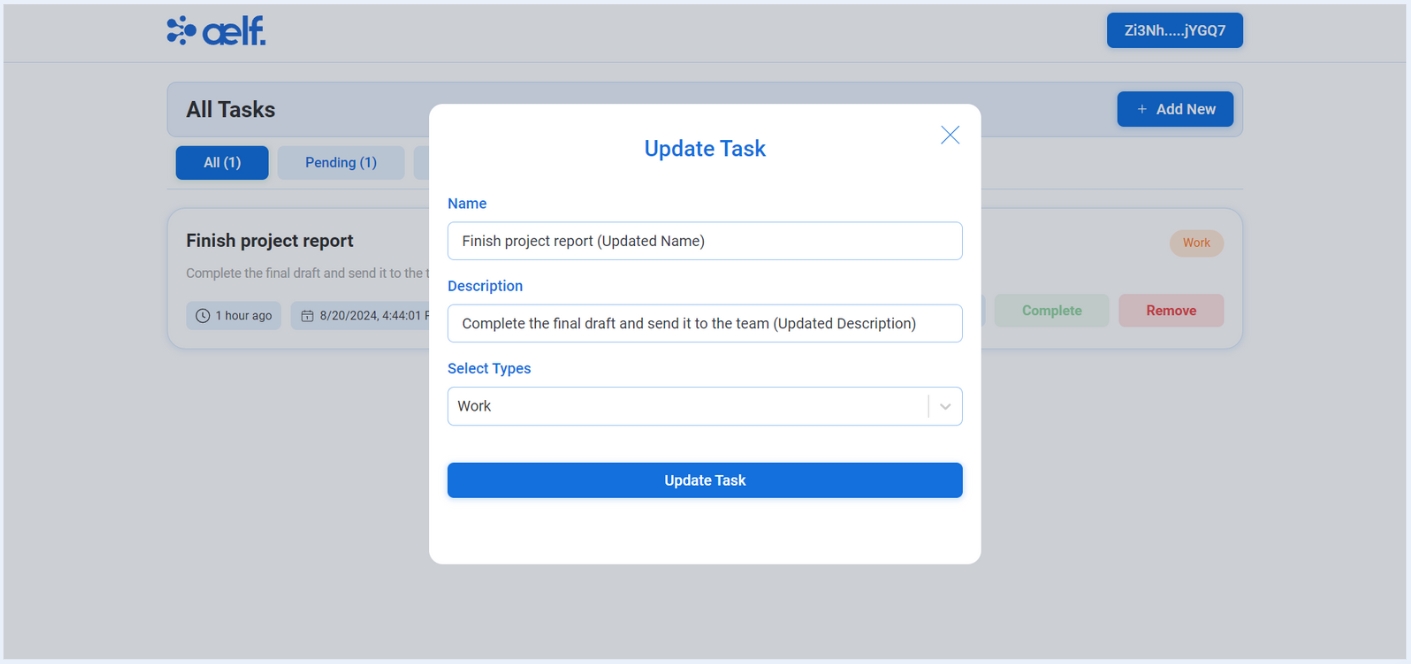
You will see the pop-up modal with form to edit the task. Edit the necessary fields according to your need.
-
Click on Update Task Button.
-
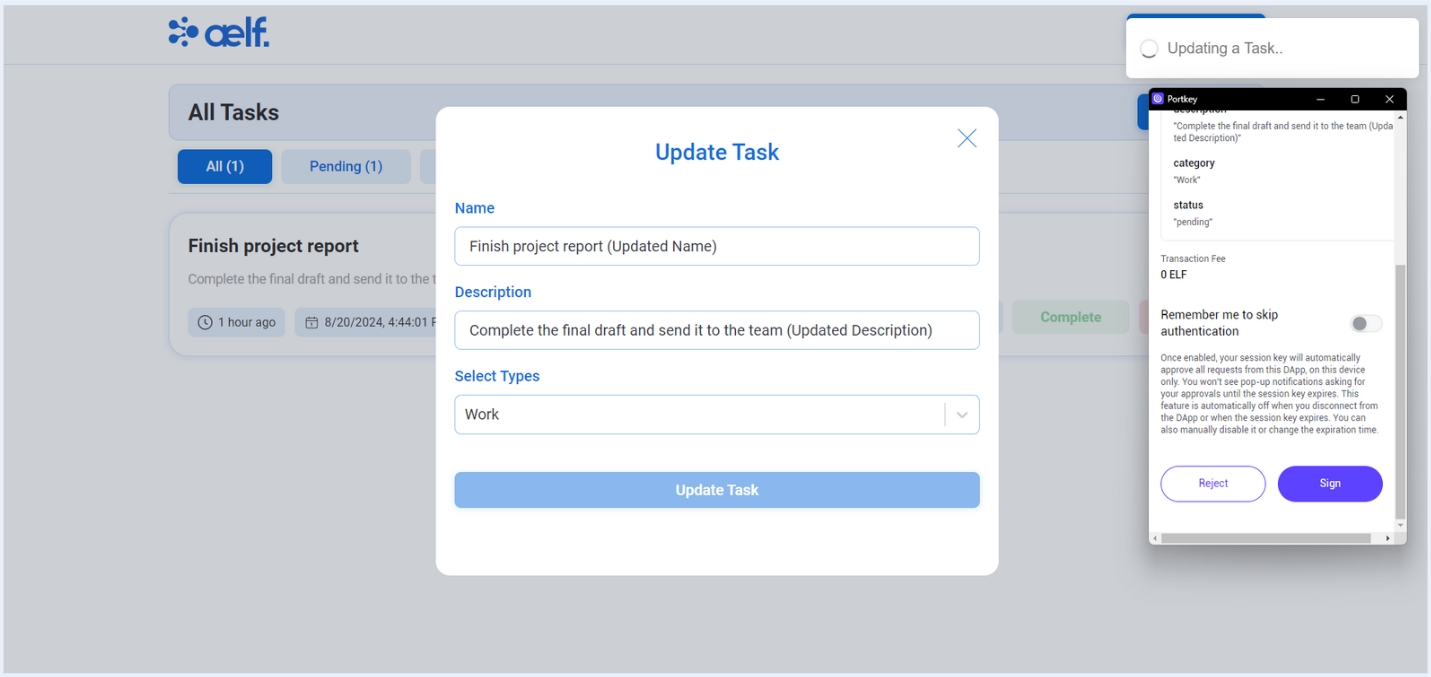
Now, You will recieve a transaction request on your portkey wallet to Sign the transaction.
-
Click on Sign the transaction.
-
After the transaction is successfully processed, your task details will be Updated✅.
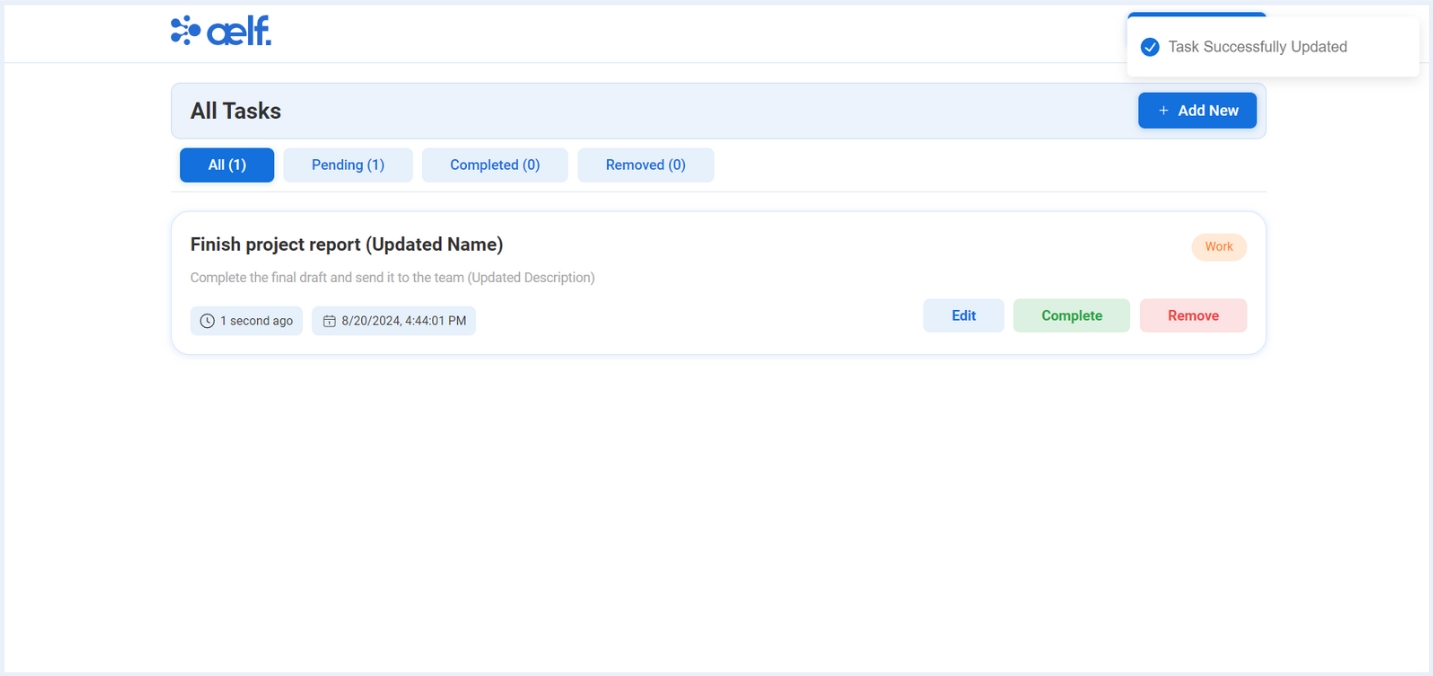
As we have Edited a Task successfully. Let's move that task to completed state.
Complete the Task
-
Click on the "Complete" button to move the task to
Completedstatus.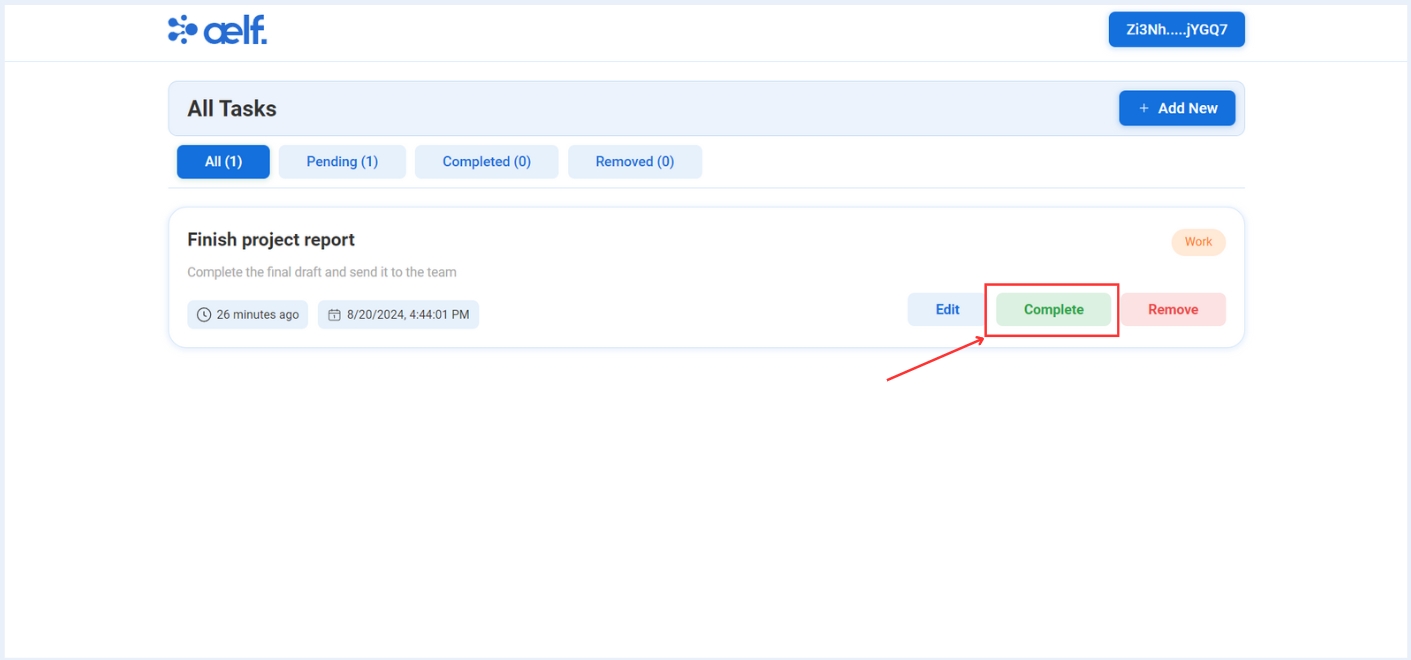
-
Now, You will recieve a transaction request on your portkey wallet to Sign the transaction.
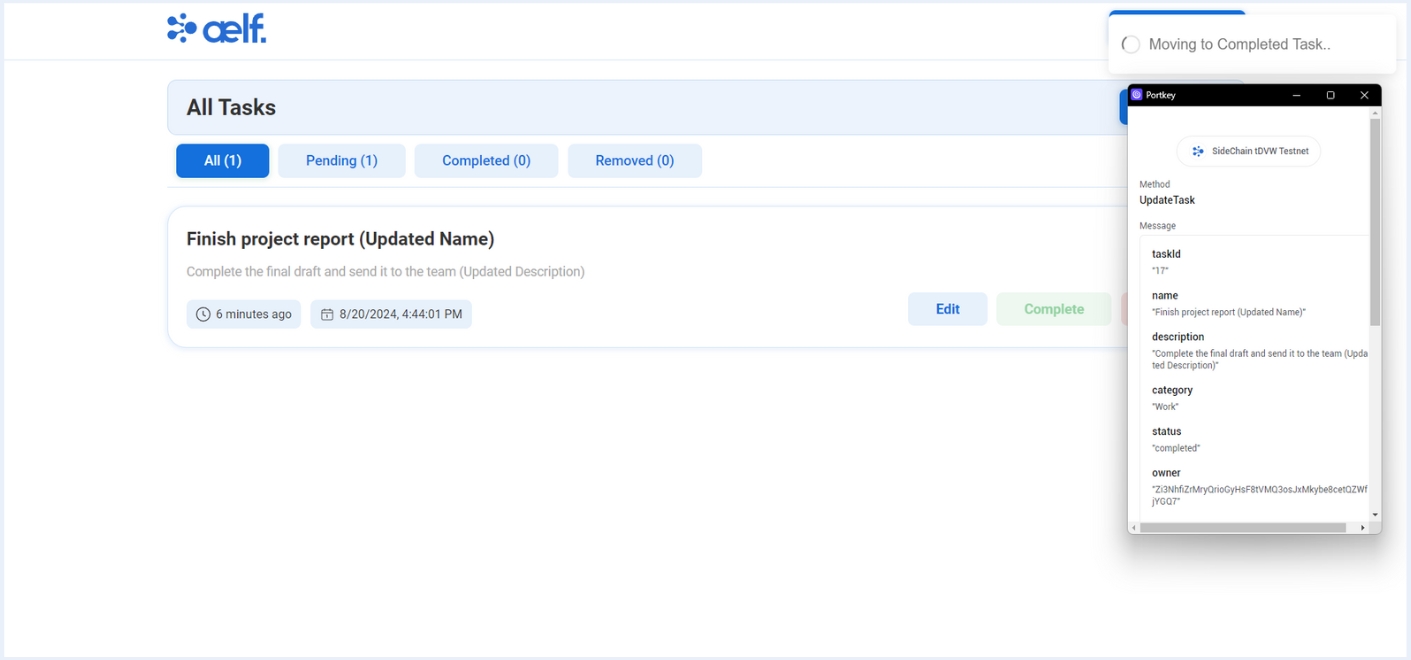
-
Click on Sign the transaction.
-
After the transaction is successfully processed, your task will be moved to the completed tab✅.
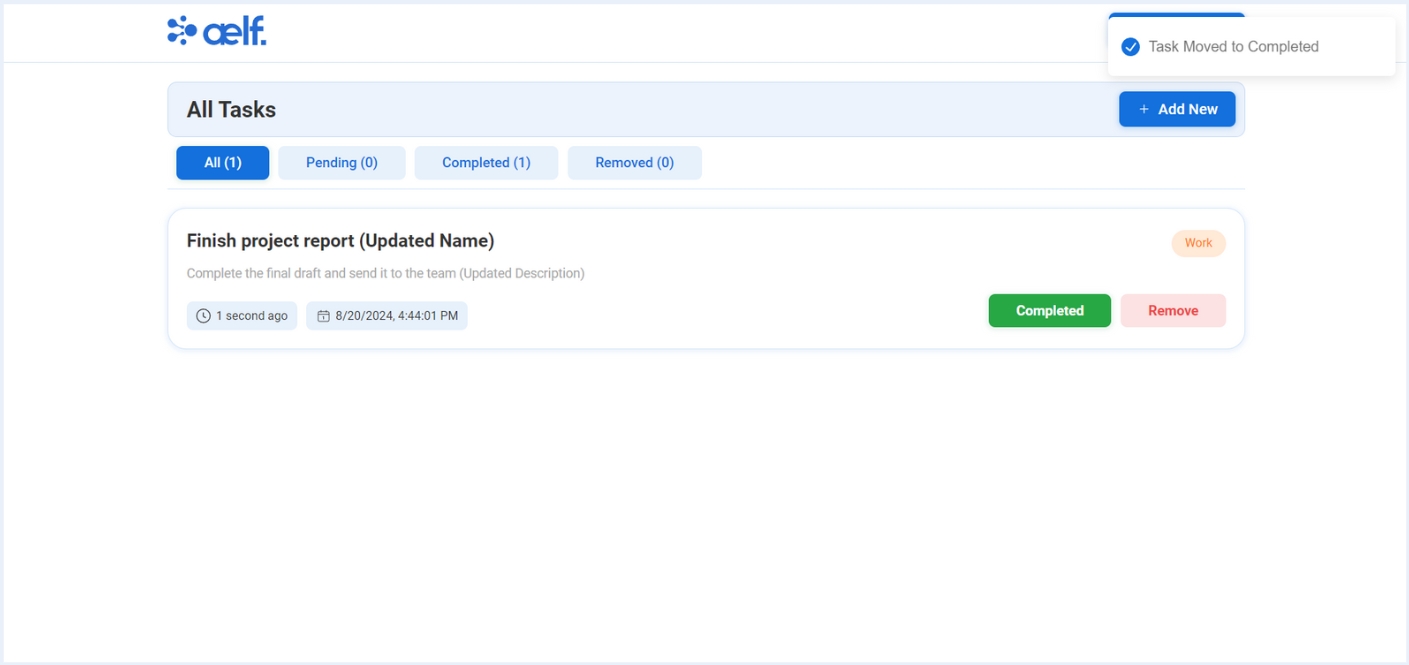
As we have performed Complete Task successfully. Let's remove the completed task.
Remove the Task
-
Click on "Remove" button to remove the task.
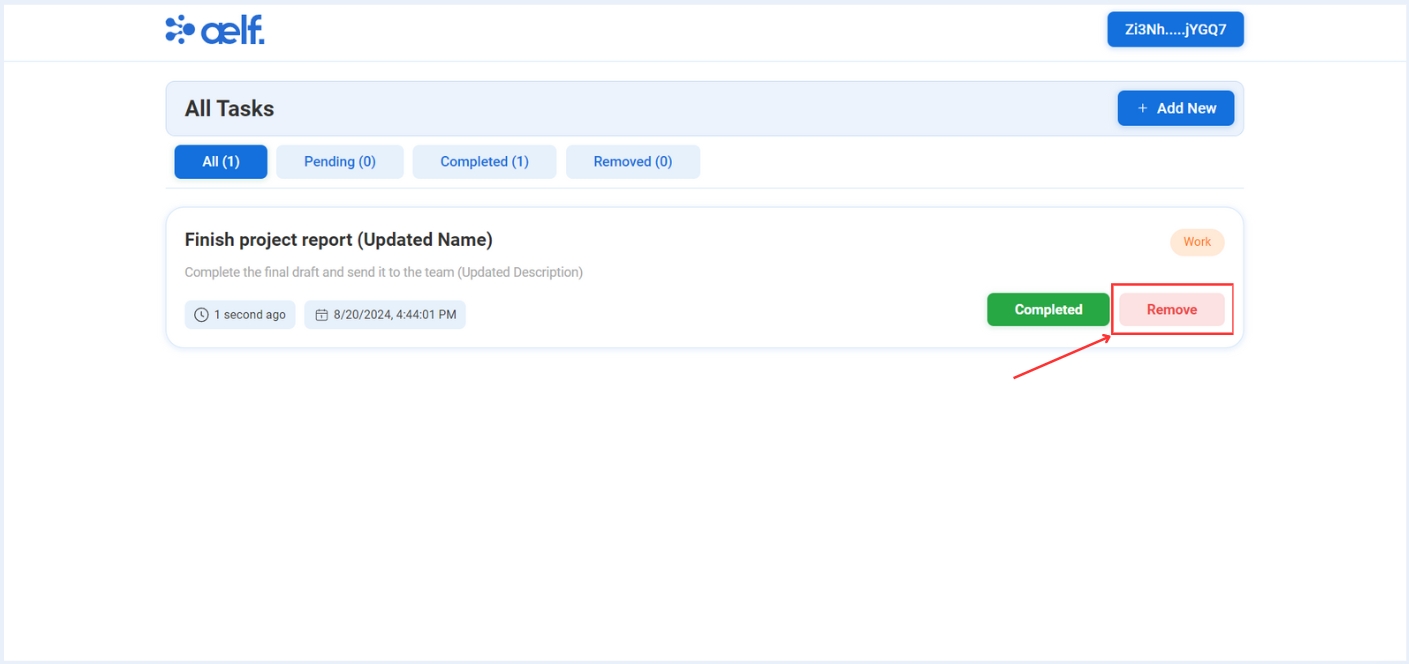
-
Now, You will recieve a transaction request on your portkey wallet to Sign the transaction.
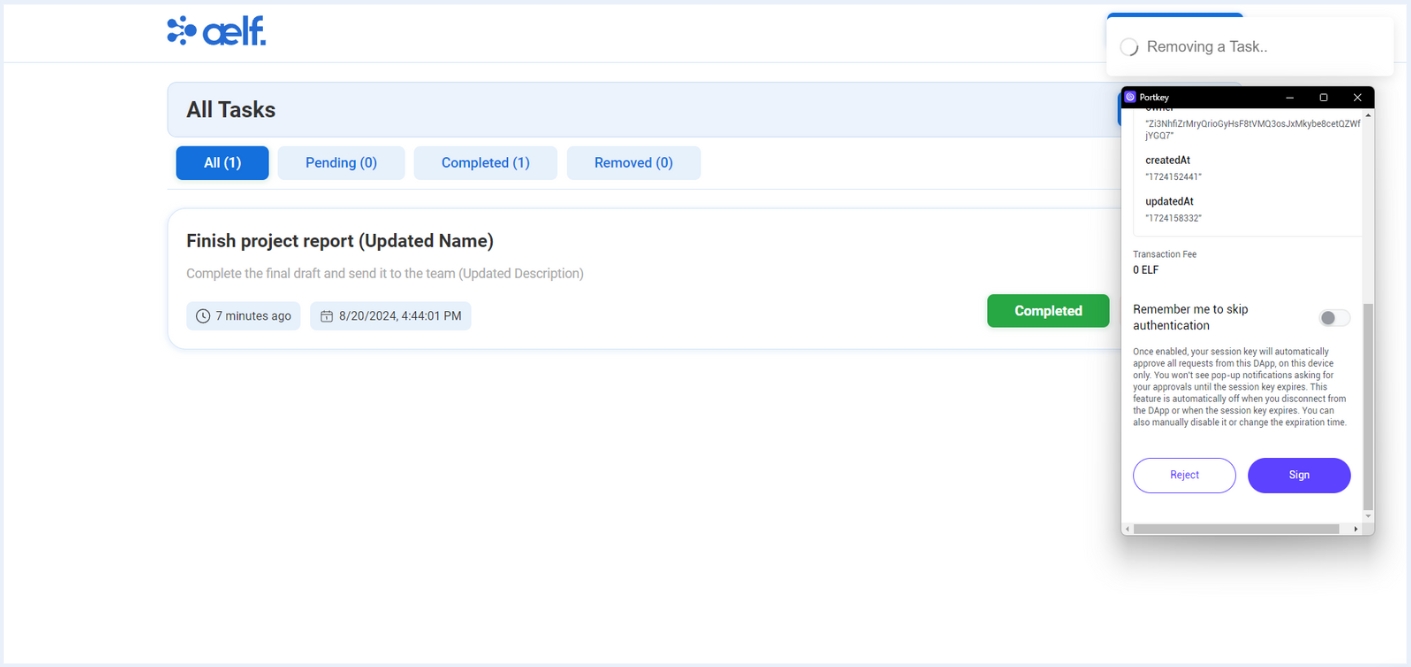
-
Click on Sign the transaction.
-
After the transaction is successfully processed, your task will be moved to the removed tab✅.
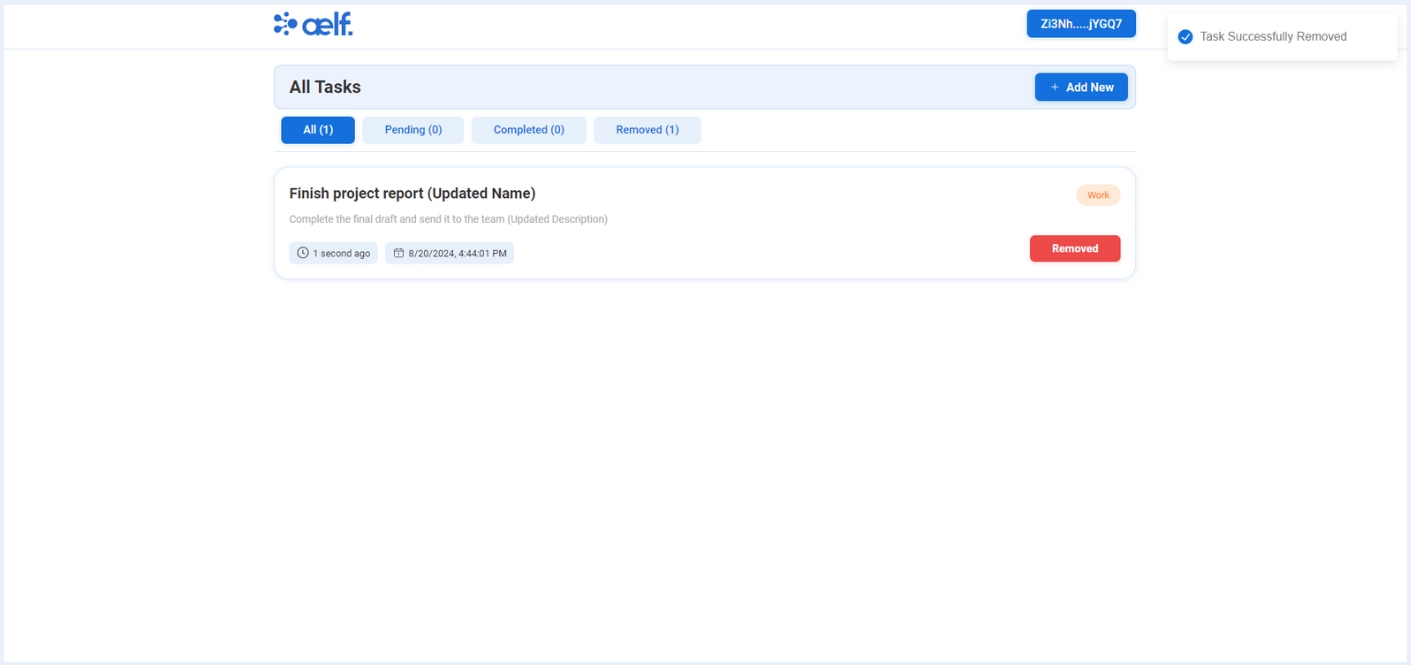
🎉 Congratulations Learners! You have successfully built your ToDo dApp.
🎯 Conclusion
🎉 Congratulations on successfully completing the ToDo dApp tutorial! 🎉 You've taken important steps in setting up your development environment, developing and deploying a smart contract on ToDo dApp, and building a fully functional ToDo decentralized application on the aelf blockchain. 🌟
📚 What You've Learned
Throughout this tutorial, you've mastered:
-
🛠️ Setting Up Your Development Environment: You prepared your workspace by installing and configuring all the necessary tools to kickstart your smart contract project.
-
💻 Developing Your Smart Contract: You created the foundation of your ToDo dApp by writing and building the smart contract that manages tasks, from creation to deletion.
-
🚀 Deploying the Smart Contract: You deployed your smart contract to the aelf blockchain, enabling its functionalities to be used in a live environment.
-
🔧 Interacting with Your Deployed Smart Contract: You connected your frontend to the blockchain, integrated Portkey for wallet connectivity, and implemented functions to manage tasks such as creating, updating, and deleting directly through the dApp.
🔍 Final Output
By now, you should have:
-
📜 A deployed smart contract that powers your ToDo dApp, managing tasks with functionalities for creation, updating, status management, and deletion.
-
💻 A fully operational ToDo dApp, allowing users to interact with the smart contract to efficiently manage their tasks.
➡️ What's Next?
With the basics under your belt, consider exploring more advanced topics:
-
📈 Enhancing Smart Contract Logic: Introduce more complex features to your ToDo dApp, such as prioritization, deadlines, or collaboration tools.
-
🔒 Improving Security: Ensure your dApp and smart contract are secure by implementing best practices and security measures.
-
🌍 Exploring Cross-Chain Features: Expand your dApp’s capabilities by exploring aelf’s cross-chain interoperability, enabling interaction with other blockchains.
The possibilities with blockchain technology and decentralized applications are endless. You're now well-equipped to take your ToDo dApp to the next level. Keep building, innovating, and exploring with aelf. 🚀
Happy coding and expanding your ToDo dApp! 😊